Japanese Food Excursion
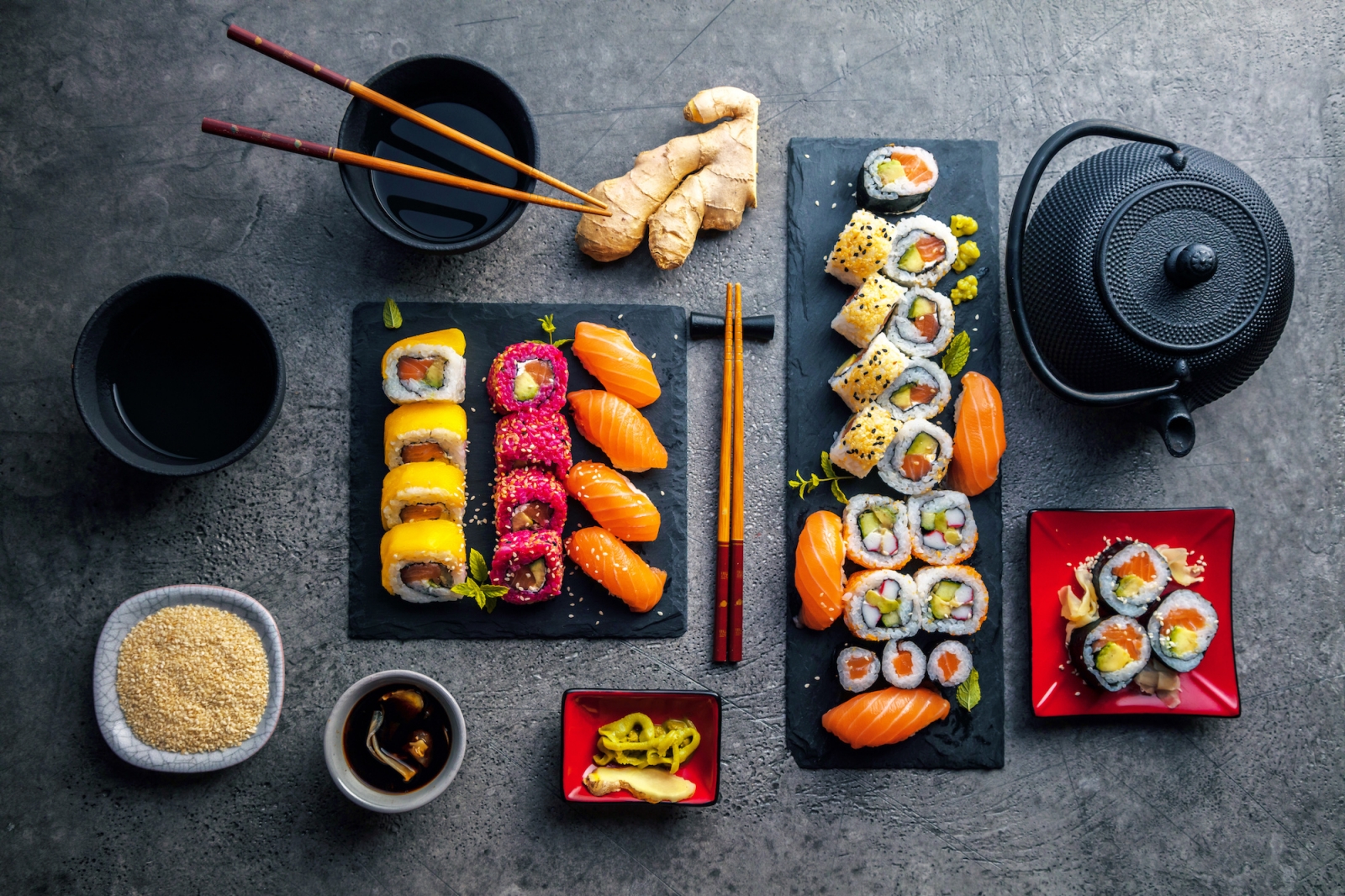
Japanese cuisine is famous worldwide for its distinctive appearance and taste. Having an aesthetically pleasing serving of varied dishes was considered just as important as the food itself. The mood of the season can be felt in the dishes served and the food should be able to provide a sense of visual satisfaction. Each Japanese dish is arranged artfully in individual dishes, plates, and bowls for each person. Sometimes, all the courses are in one time and consumed in no particular order.

It is not always easy to navigate between the huge variety of local food options, that is why on our website we recommend to you find a local private English-speaking tour guide in Tokyo who will not only show you the country but explain all the nuances of the local cuisine, recommend the most authentic eateries and particular dishes and even teach you how to use them like a local!
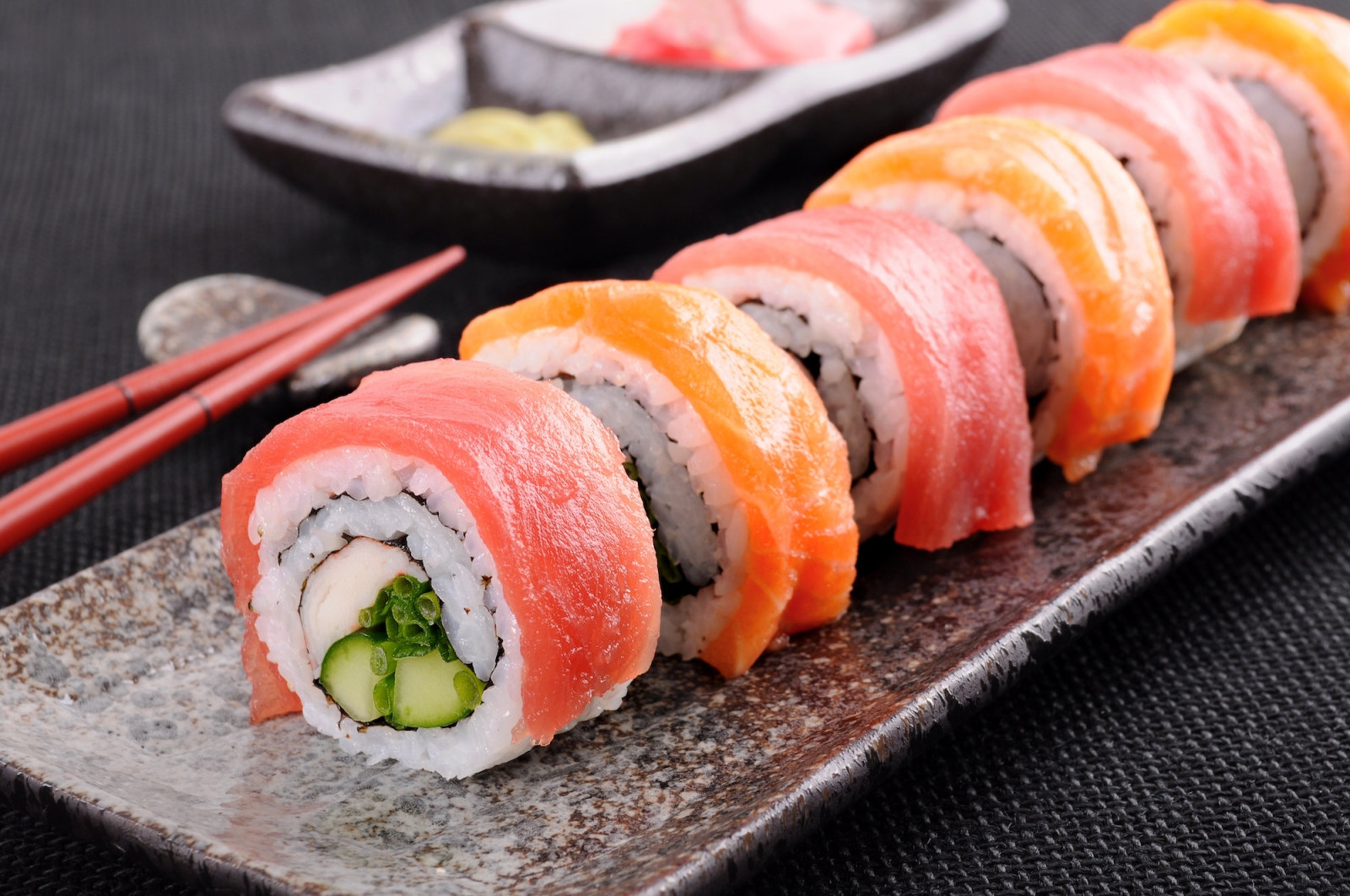

Japan consists of 4 main islands. The total size, population, and location of the country, all combined to demand much of the food come from the ocean, and the world's roving fishing fleets admirably supply that need. It’s estimated that over 30 kg (70 lbs) of seafood every year is consumed by the Japanese people. Among the many different ways of preparing fish, the most popular ones are frying, and presenting them raw, as in sushi and sashimi. Possibly sushi, the bite-sized pieces of raw fish meat pressed onto a ball of vinegar-flavored rice and shrimp, tempura and vegetable coated with egg batter and deep fried, as the best known to the westerners. The meat dishes were only introduced in Japanese as a Western Cuisine.
Japanese History Cooking Tours
Many years ago, before the influence of the westerners, each community in Japan has its own traditions. Similar to the traditions in other countries and continents, Japan is popularly known for its traditional food and culture. Restaurant owners, chefs, or any food lovers including local tour guides in Tokyo, Kyoto, Osaka, and other cities are familiar with Japanese cuisine. Some of the well-known Japanese cuisine locally and outside the country include sashimi, sushi, buckwheat noodles, and tempura. These foods are based mainly on the combination of staple food, usually with steamed rice, and a number of main and side dishes. Traditional Japanese cuisine also comes with clear miso soup and pickles. Another very unique characteristic of Japanese cuisine is the fact that some of their ingredients are used only by season, making it totally dependent on nature.
Tour for Japanese gourmet food
When it comes to the serving of dishes, Japanese food is served in a way that greatly opposes other countries where pots, large saucepans, and plates were placed in the middle of the dining table. On the other hand, Japanese cuisine is served in a very unique style. The rice is solely served in one small bowl per person and the side dishes were served in separate bowls or plates.
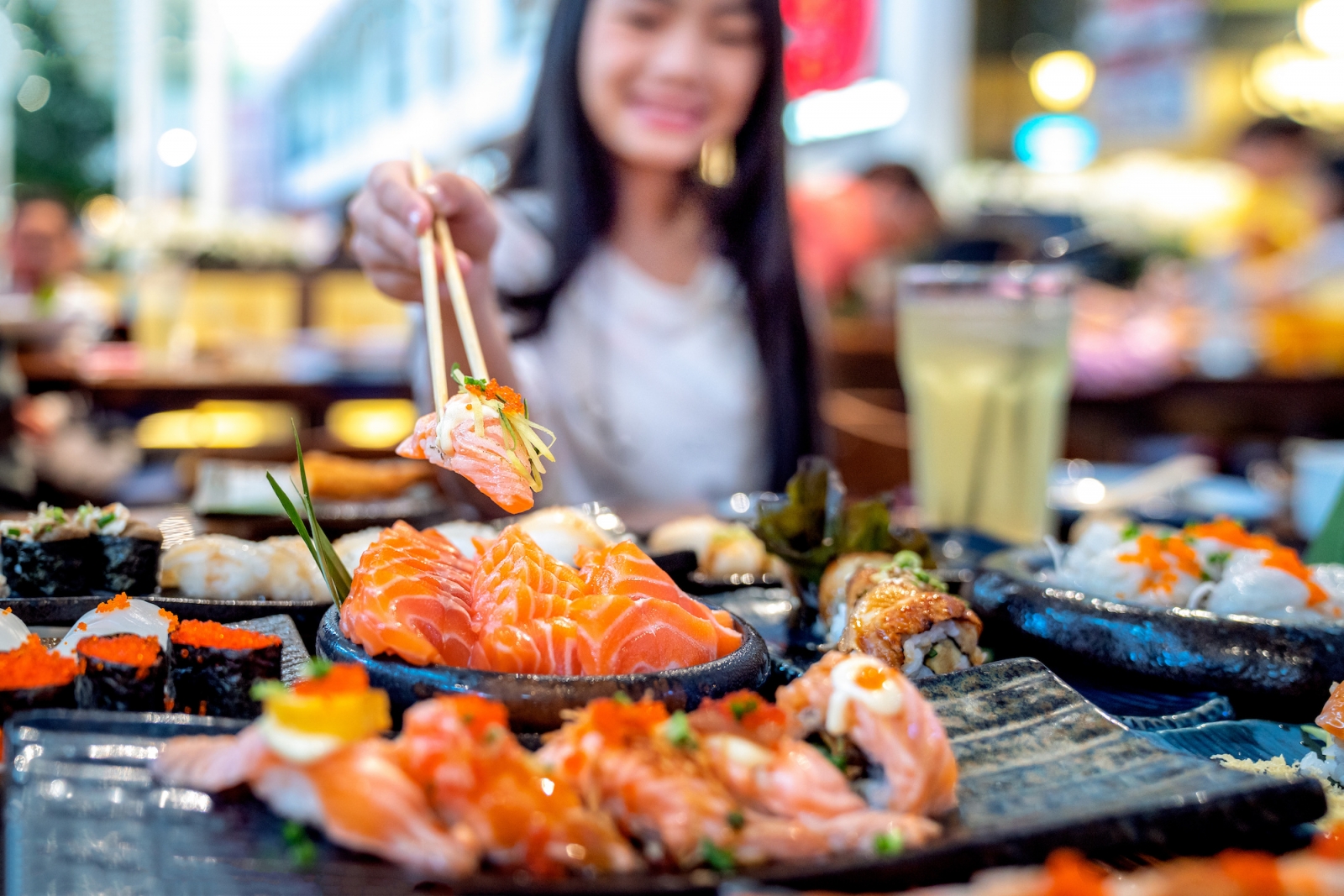

Well, of course, everyone uses his or her own plates or bowls. According to their tradition, different dishes aren’t supported to be mixed or in contact with each other and that is the reason why every dish in Japan is served in its own bowl or plate. Alternatively, dishes can be served in partition through the use of leave. One example of this is in the tamagoyaki preparation, where the fish and eggs are carefully separated. During the olden days, every meal was brought in serving trays and it’s very common to see the faldstool tray being used. This is why when you travel, for example, to Hokkaido it is better to find a local private tour guide in Sapporo who will teach you the northern Japanese cuisine, and when you go south, the best option is to find a local English-speaking tour guide in Hiroshima because the southern cuisine has some unique features.
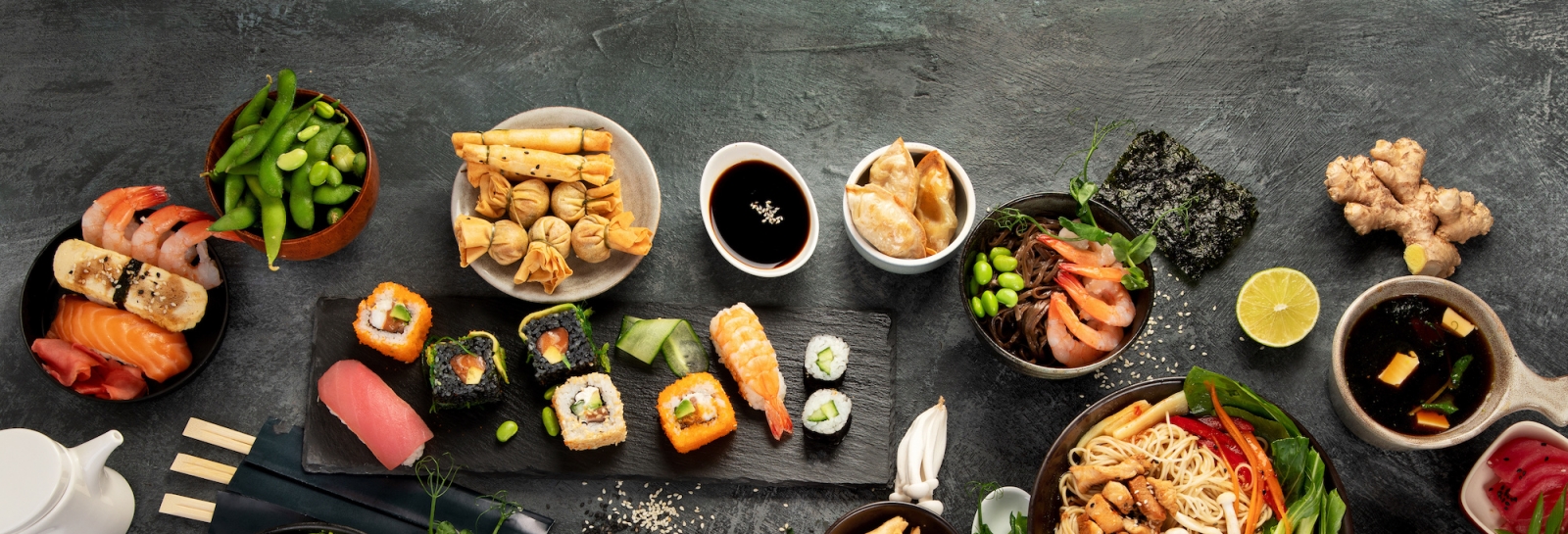

Traditional Japanese is characterized by the use of rare meat, fats and oils, and dairy products. The use of soy sauce leads to the high content of mineral salts in a lot of their traditional cuisines. The less meat consumption comes from the fact that the citizens are always taking great advantage of the abundance of seafood supply because the country is an island. The Japanese diet mainly consists of grains, seaweed, and vegetables. On the other hand, red meat is rare in Japanese meals. When preparing Japanese meals, the fat and oil are used in very small amounts and the foods were usually flavored through the use of additives such as mirin and sake, soy sauce, sugar, salt, and vinegar.
Japan's local Food Tasting Tours and excursions
Herbs and spices were also very popular additives in Japanese meals and are mostly used in order to clean or hide the sour taste of raw fish. The salads were also served as a common side dish. Japanese cuisine has incorporated many different food preparation methods, which include, simmering, grilling, deep frying, and steaming. There are many other ingredients that were eaten raw. One important thing to keep in mind is that the Japanese have attached a lot of importance to their cooking methods, with each dish having its own special way of preparation. Some local English-speaking tour guides in Kobe can teach you to buy the right fresh meat and fish from the market as well as share the best cooking recipes.

If you haven’t yet tasted any Japanese cuisine, you should consider visiting the nearest Japanese restaurant to you. When you decide to do this, you will surely have a very unforgettable experience and our local English-speaking tour guide in Yokohama or other cities of Japan are always at your disposal in this very complicated but so tasty activity as food tour degustations! If you plan on going on a vacation, consider going to Japan and you will competently love it.
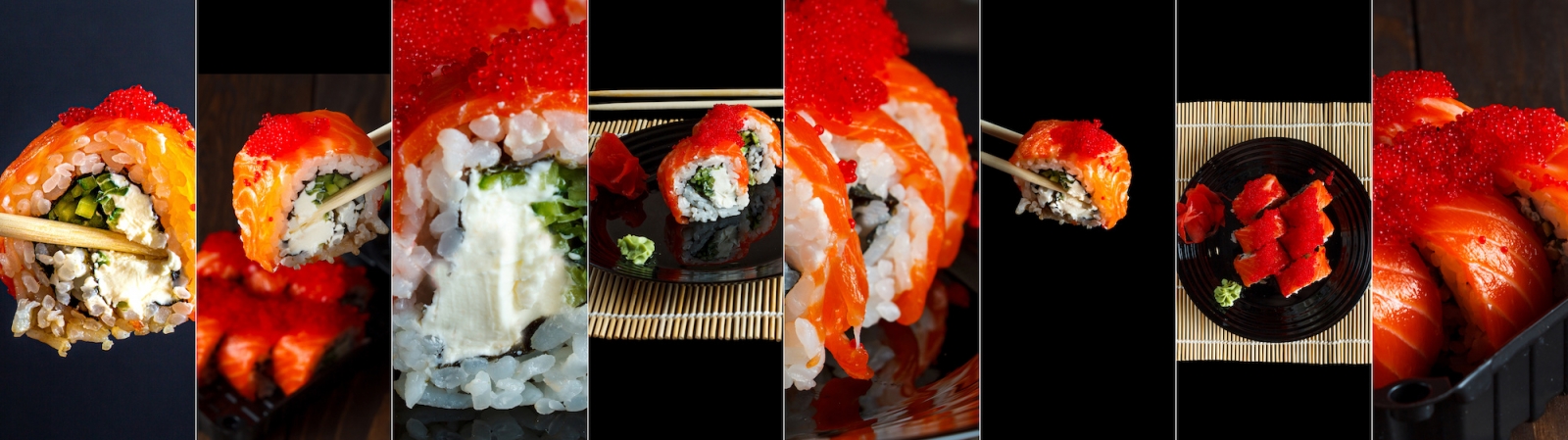

General Characteristics of Japanese cuisine
- Japanese cuisine is known for its emphasis on fresh, seasonal ingredients, delicate flavors, and beautiful presentation. It is a diverse and sophisticated cuisine that has been refined over centuries and has become popular all over the world.
- One of the defining features of Japanese cuisine is the use of raw or lightly cooked ingredients, such as sushi and sashimi. Other popular dishes include ramen (noodles in a savory broth), tempura (lightly battered and fried seafood or vegetables), udon (thick noodles in a broth), soba (buckwheat noodles), donburi (rice bowls with various toppings), and yakitori (grilled skewers of chicken).
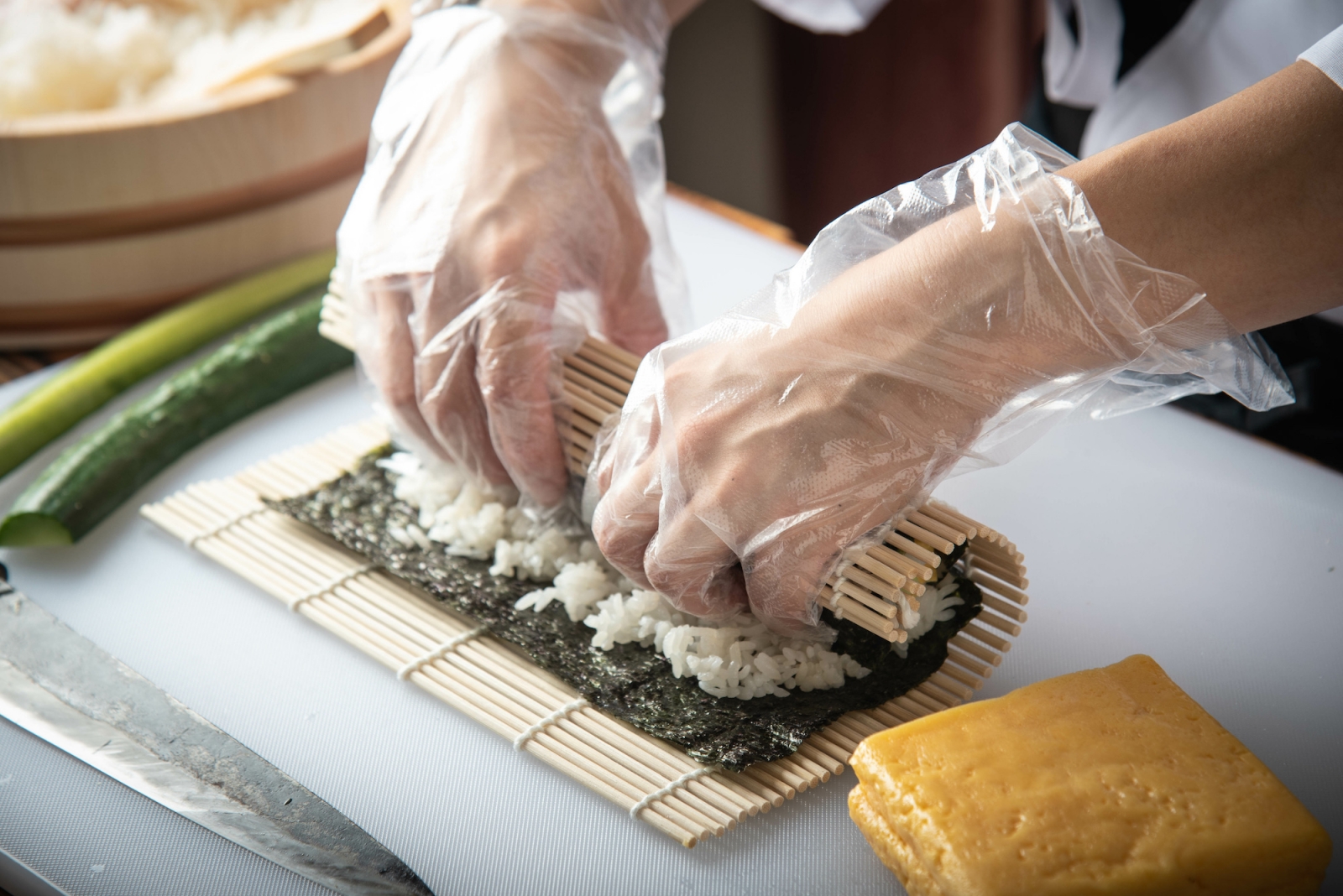

- Traditional Japanese cuisine also includes a variety of seasonal dishes, such as hot pot dishes in the winter and chilled dishes in the summer. Tea is also an integral part of Japanese cuisine, with various types of tea served with meals or as a beverage on their own.
- Japanese cuisine places great importance on the presentation of dishes, with a focus on balance, harmony, and simplicity. Many Japanese dishes are served in small portions, and the use of colorful and attractive ingredients is common.
- Japanese cuisine is a unique and sophisticated cuisine that has become popular all over the world, known for its fresh ingredients, delicate flavors, and beautiful presentation.
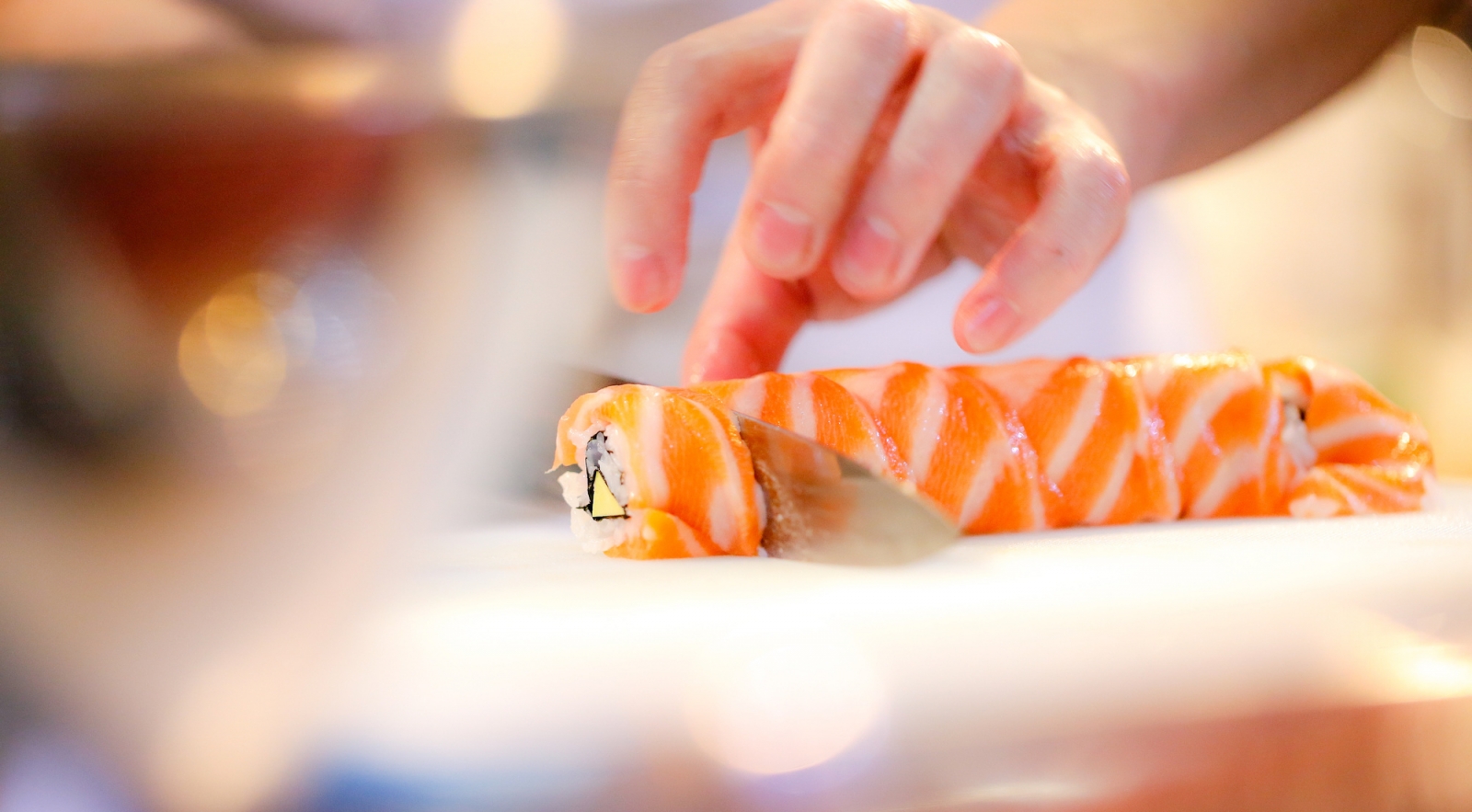

Geographical influences on Japanese cuisine
The cuisine in the north and south of Japan can be quite different due to differences in climate, geography, and historical influences. Here are a few examples:
- Hokkaido, the northernmost island of Japan, is known for its seafood, dairy products, and hearty comfort food. Due to its cold climate, stews, soups, and hot pots are popular, and dairy products like milk, cheese, and butter are used more commonly than in other parts of Japan. Hokkaido is also known for its seafood, such as salmon, crab, and sea urchins.
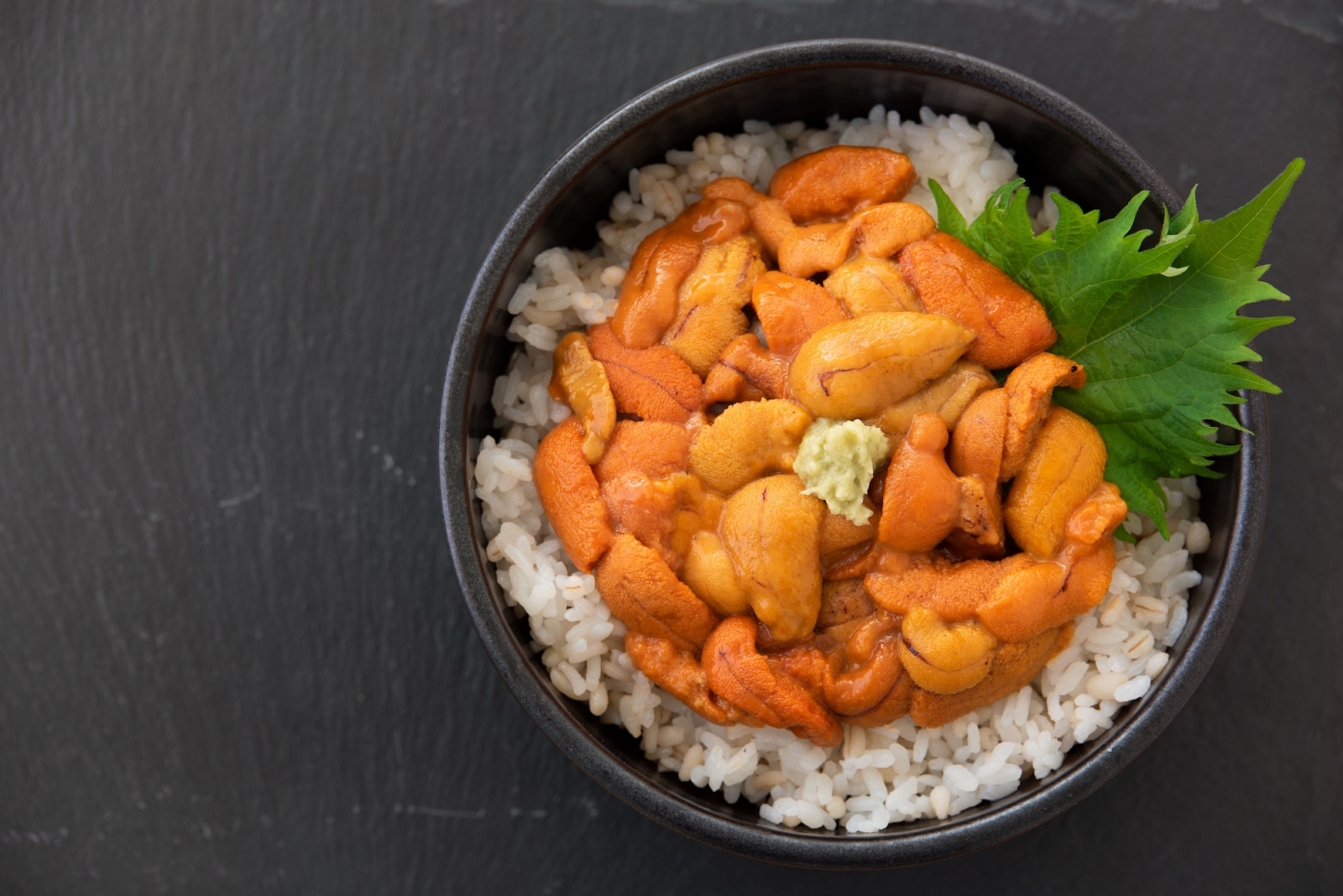

- On the other hand, Okinawa, the southernmost prefecture of Japan, has a cuisine that is influenced by its subtropical climate and location. Okinawan cuisine incorporates a lot of vegetables, tofu, and seafood, and is known for its unique dishes such as goya champuru (stir-fried bitter melon), andagi (Okinawan-style doughnuts), and Okinawa soba (noodles in a pork broth).

- Other regions of Japan also have their own unique local specialties. For example, Kyoto is known for its traditional kaiseki cuisine, which emphasizes the use of seasonal and local ingredients and is presented in a multi-course format. Hiroshima is known for its okonomiyaki, a savory pancake filled with cabbage, meat or seafood, and noodles, while Osaka is known for its takoyaki, small balls of dough filled with octopus and other ingredients.
The cuisine of Japan varies greatly from region to region and offers a wide variety of flavors, ingredients, and cooking styles. Do not hesitate to question your local private English-speaking tour guide in Japan about the regional popular dishes in every prefecture.

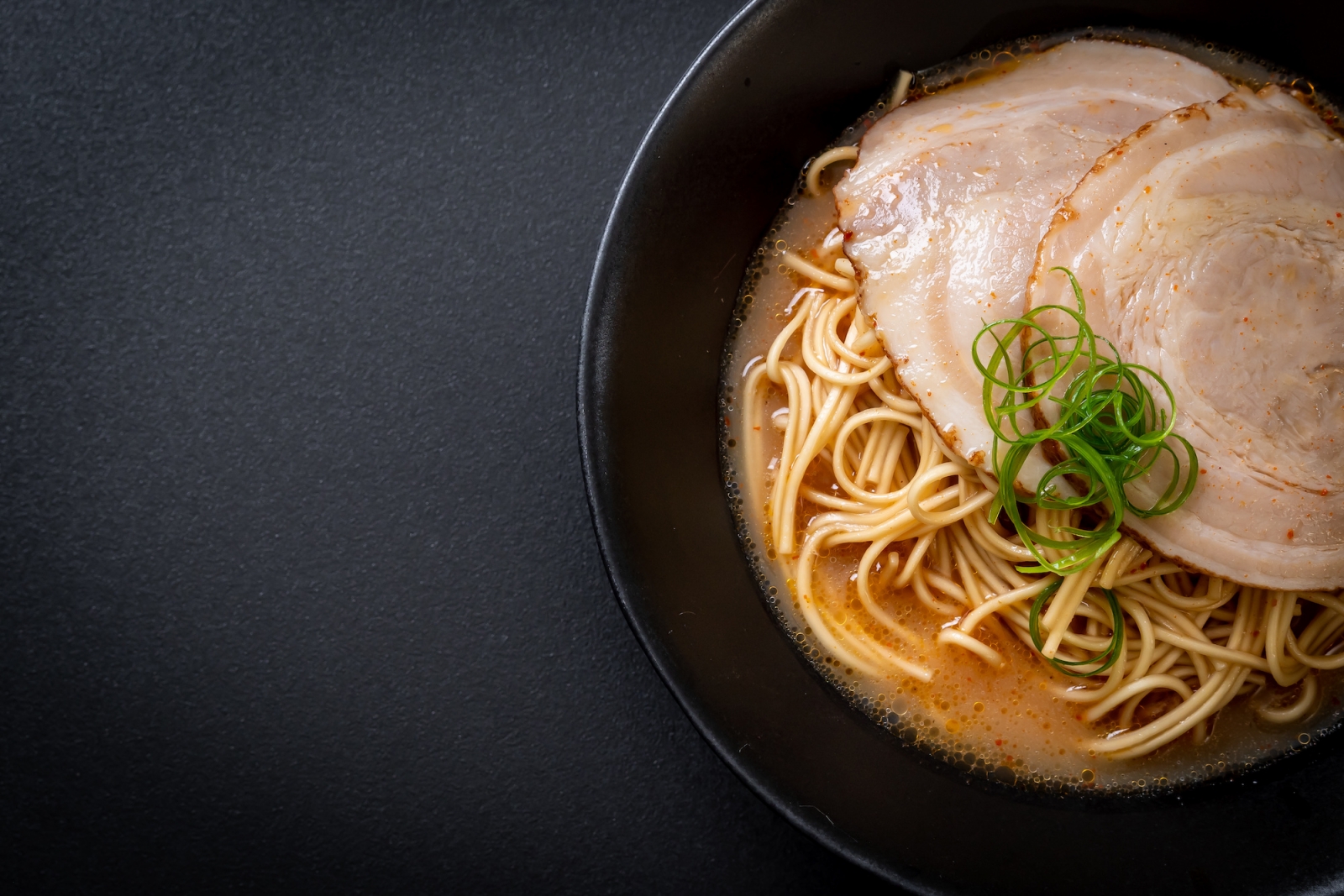
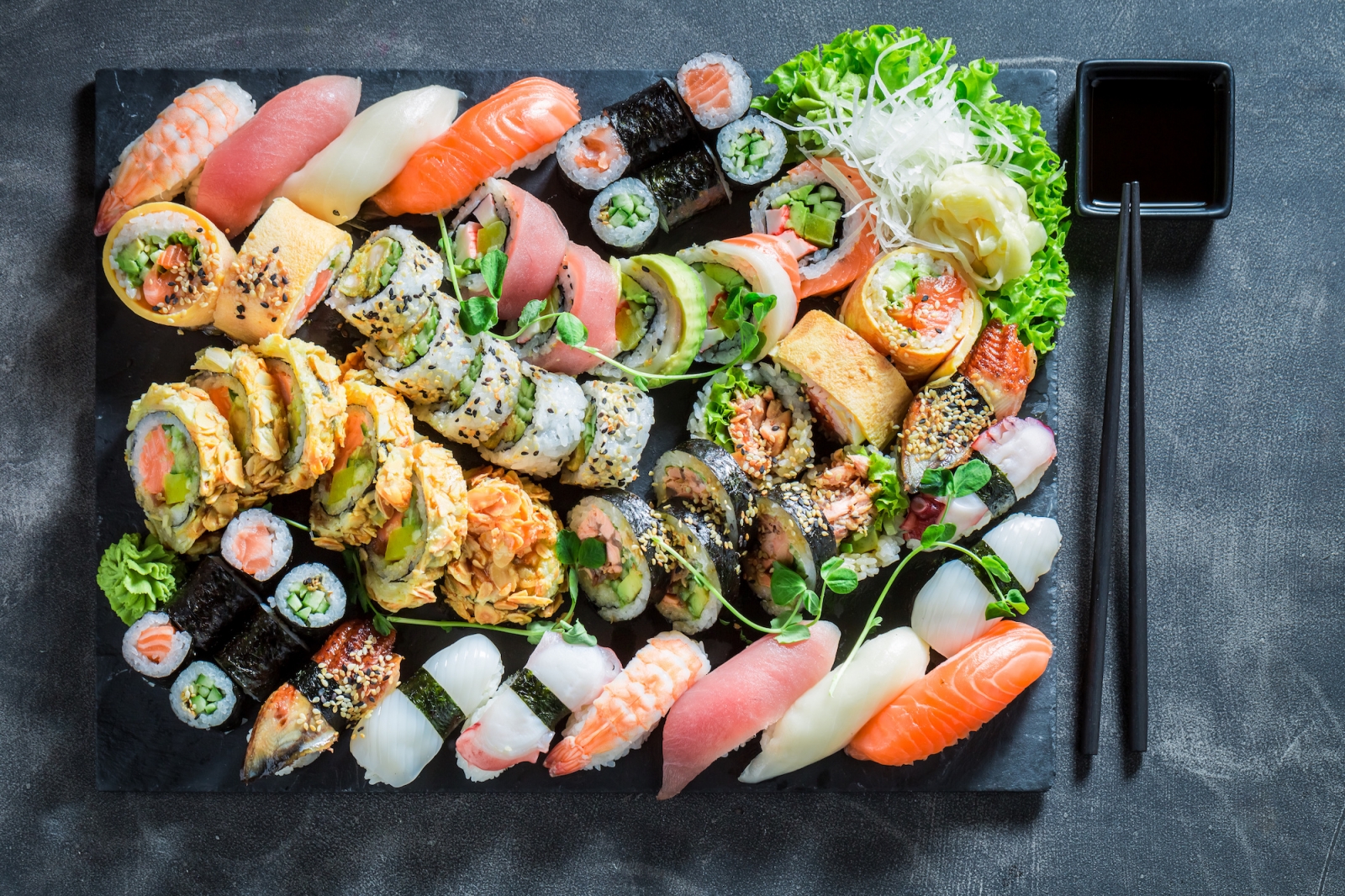
The most popular Japanese dishes
Japan has a wide variety of popular dishes that are enjoyed both domestically and around the world. Here are a few of the most well-known:
- Sushi is perhaps the most famous Japanese dish, consisting of vinegared rice topped with various ingredients such as raw or cooked seafood, vegetables, or egg. It is often served with soy sauce, wasabi, and pickled ginger.

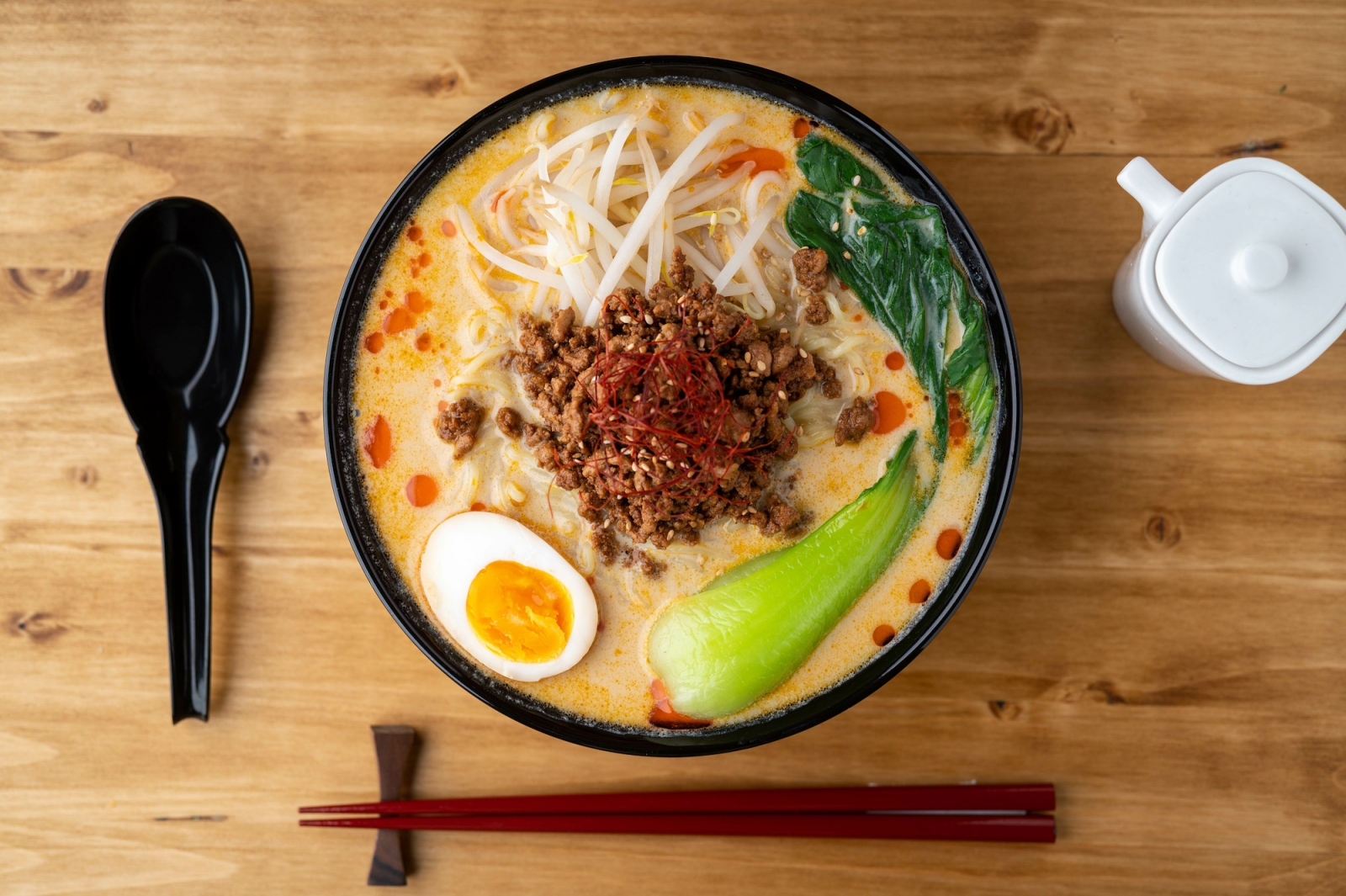
- Ramen is a noodle soup dish that typically consists of Chinese-style wheat noodles in a savory broth, topped with various ingredients such as sliced pork, boiled egg, and scallions.

- Tempura is a dish consisting of battered and deep-fried seafood, vegetables, or other ingredients. It is often served with a dipping sauce made from soy sauce, dashi, and other seasonings.
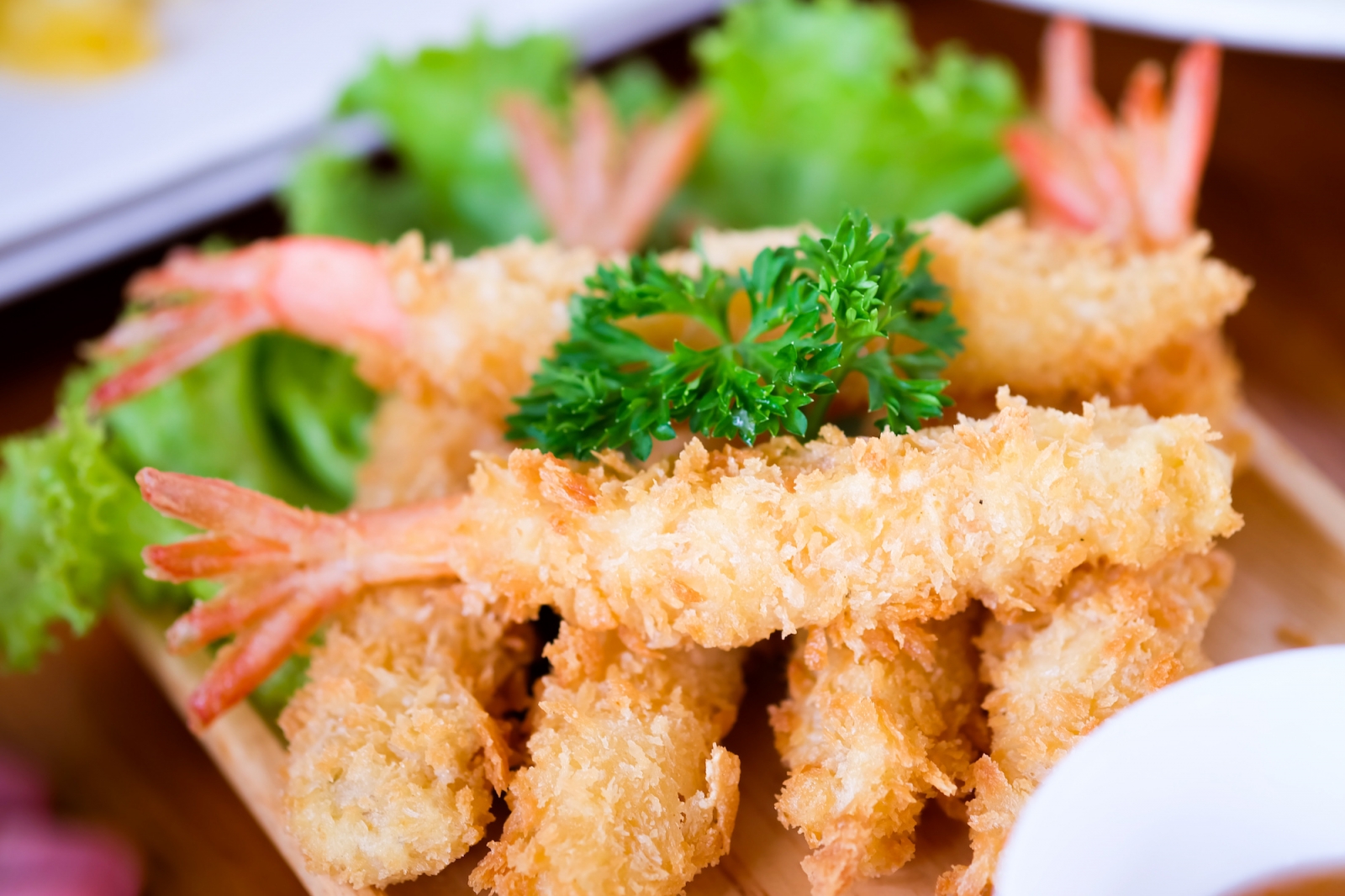

- Udon is a type of thick wheat noodle that is often served in a hot broth, such as dashi, with various toppings such as sliced beef, tempura, or vegetables.

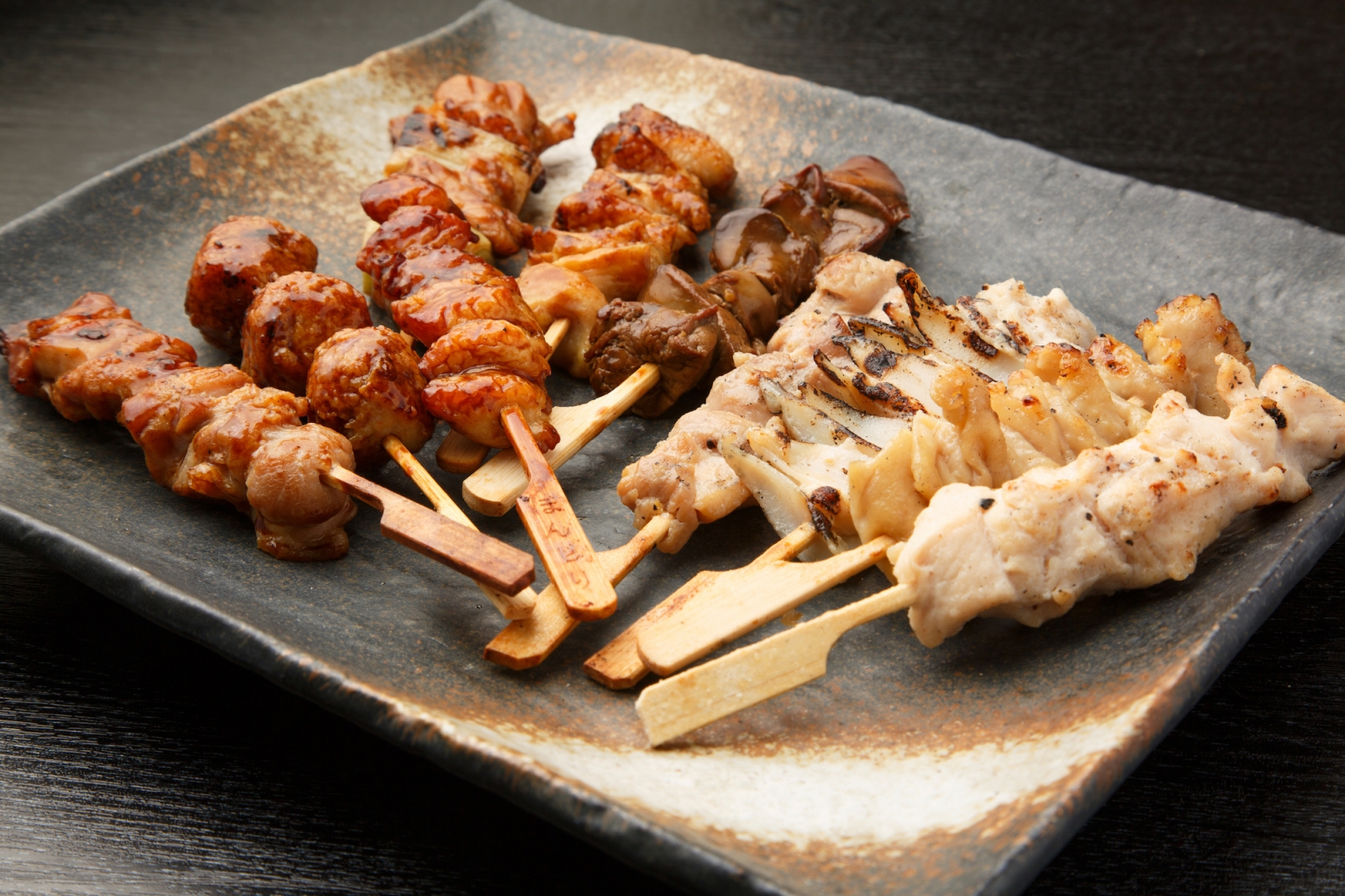
- Yakitori is a popular street food consisting of skewered and grilled chicken that is seasoned with salt or a sweet soy-based sauce.

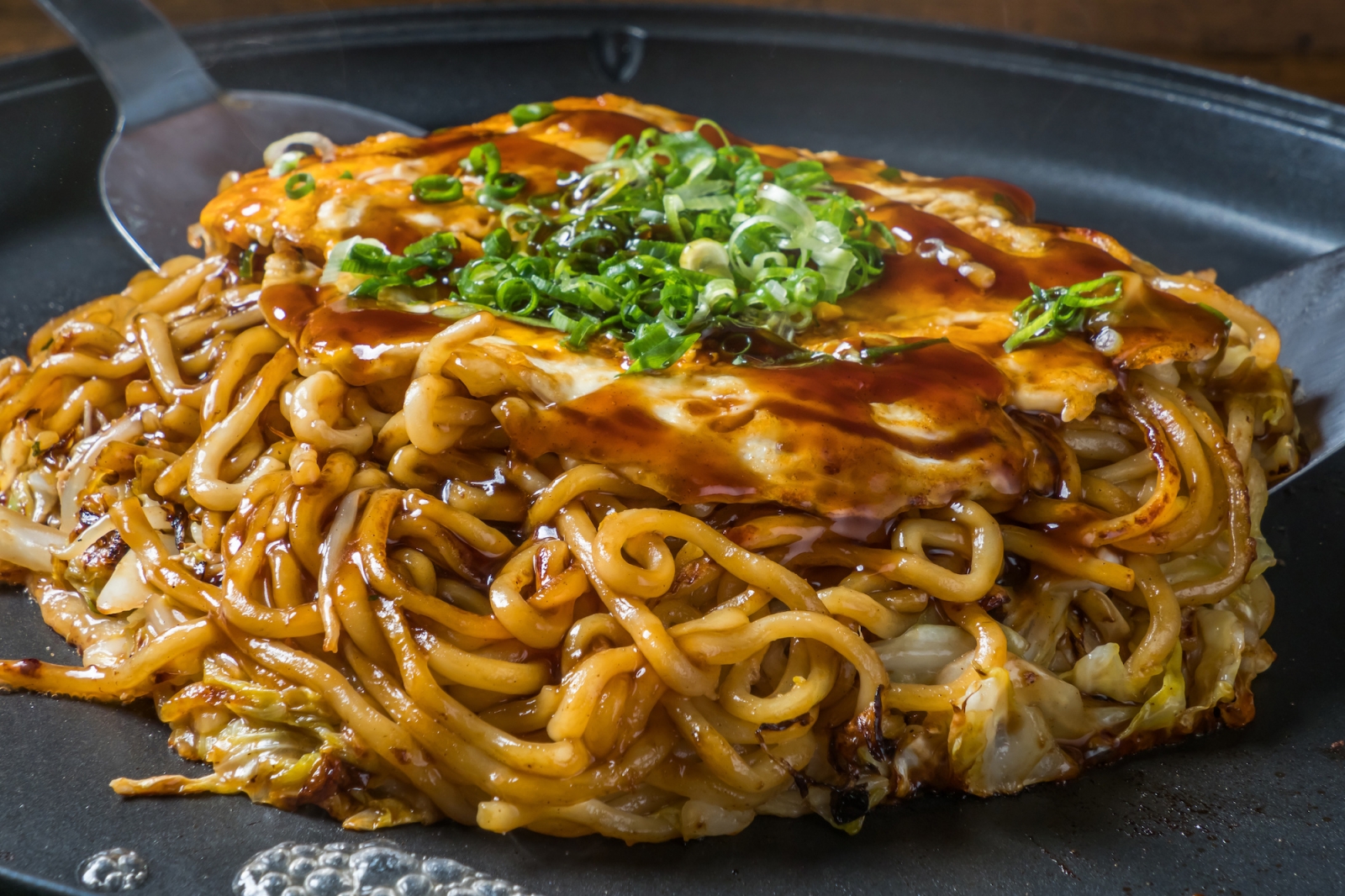
- Okonomiyaki is a savory pancake made with flour, eggs, shredded cabbage, and various other ingredients such as pork belly, seafood, or cheese. It is typically served with a variety of toppings, such as mayonnaise, okonomiyaki sauce, and bonito flakes.

- Tonkatsu is a breaded and deep-fried pork cutlet that is often served with a sweet and tangy sauce and shredded cabbage.
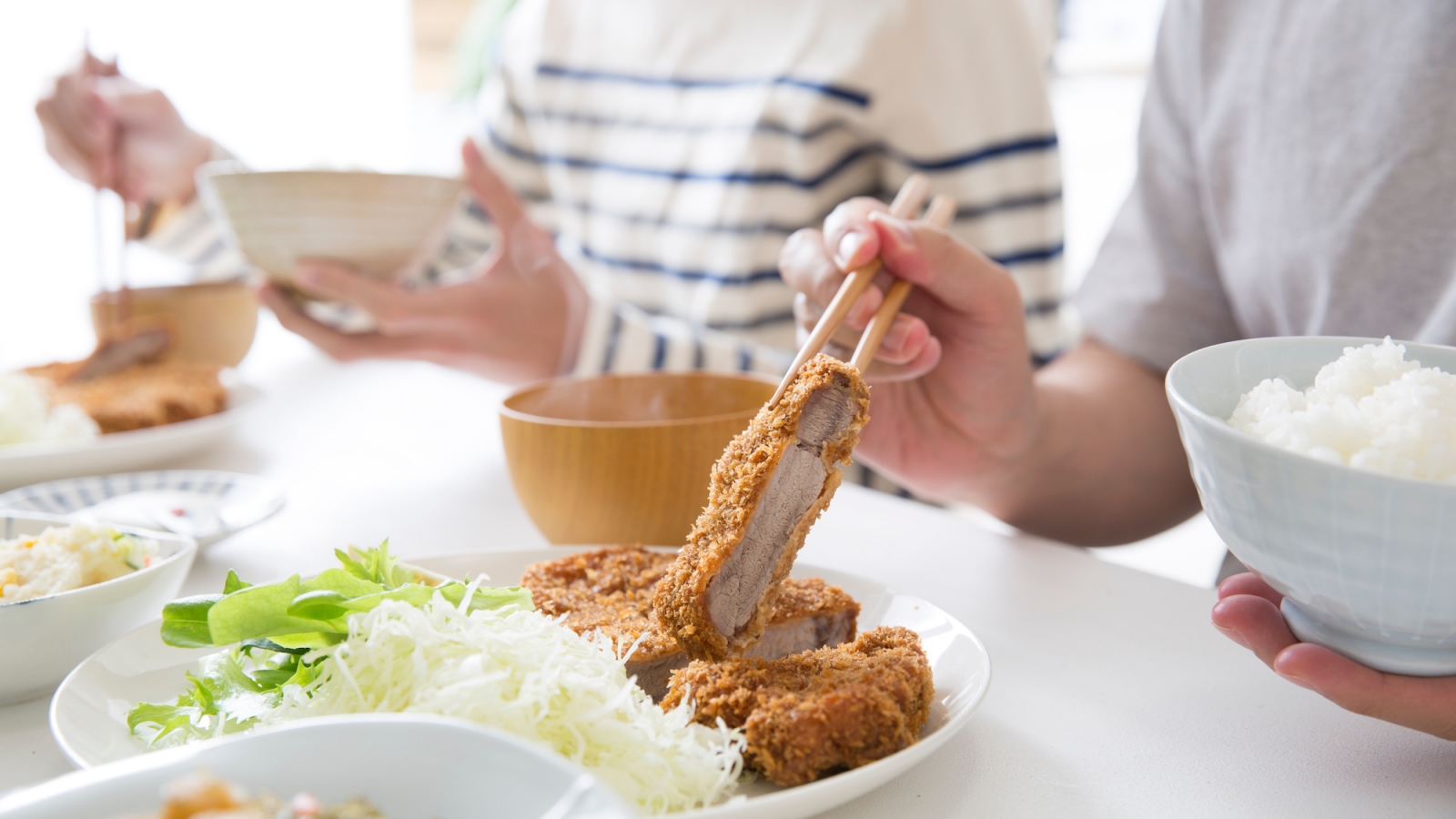

These are just a few examples of the many delicious dishes that are popular in Japan. Each dish has its own unique flavor and style, and there are countless regional variations to discover as well.
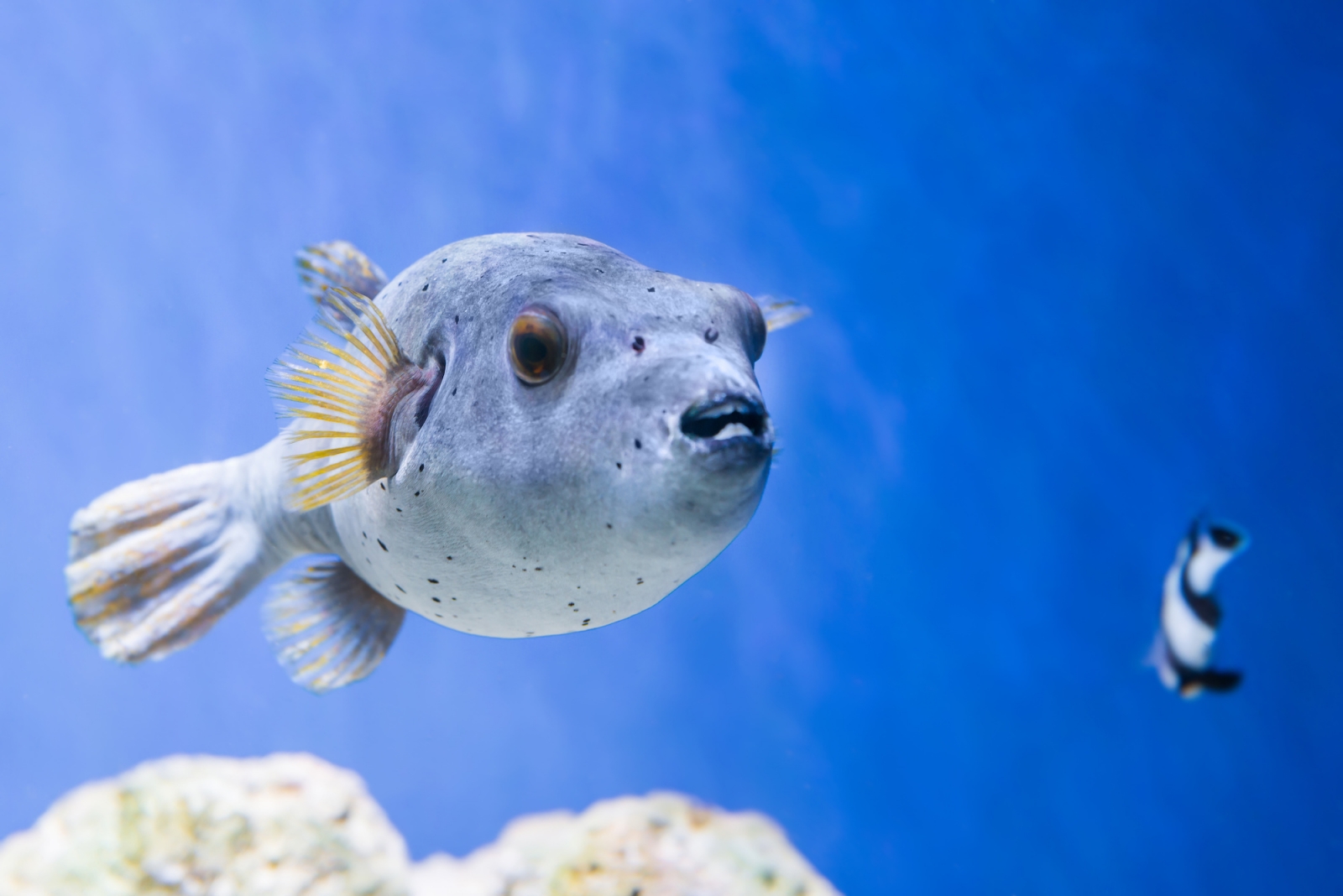
Poisonous but so tasty Fugu fish
Fugu, also known as pufferfish, is a type of fish that is considered a delicacy in Japan. However, it is also one of the most poisonous fish in the world, with certain parts of the fish containing a deadly toxin called tetrodotoxin.

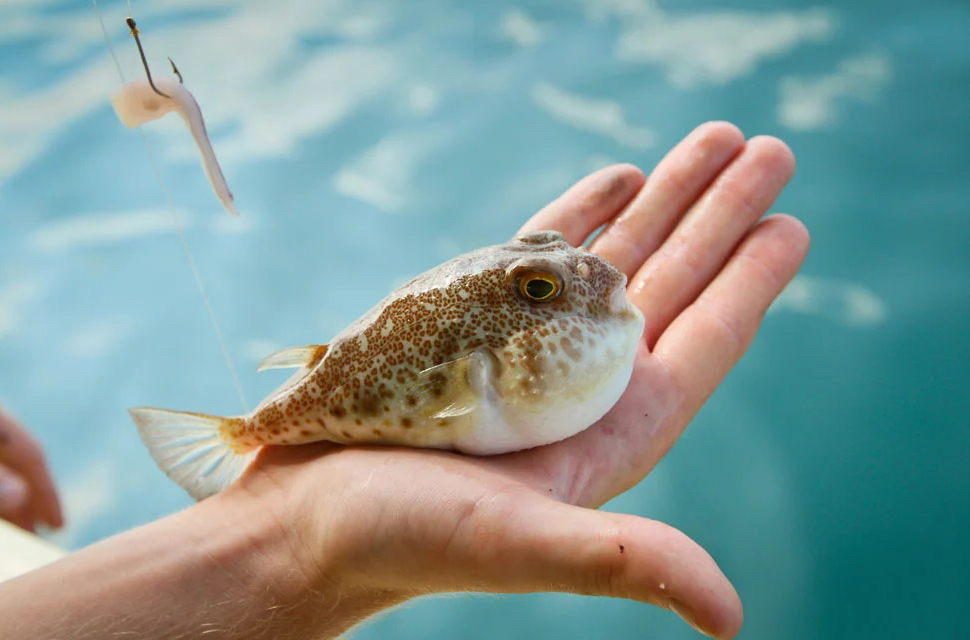
Catching and preparing fugu is tightly regulated in Japan, and only licensed and highly trained chefs are permitted to serve the fish. These chefs must undergo several years of apprenticeship and training to learn how to properly remove the toxic parts of the fish and prepare it safely.
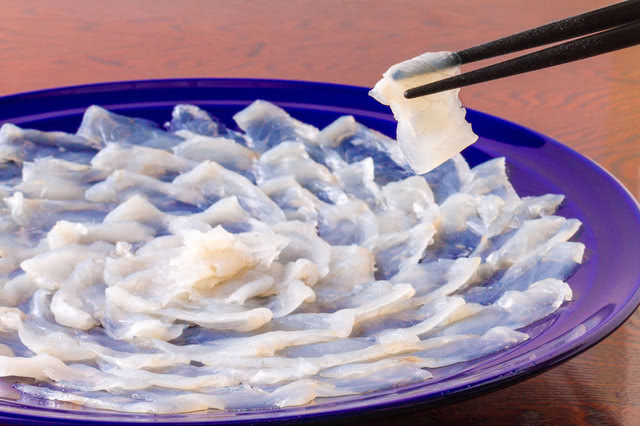
The preparation of fugu is a delicate process that requires careful attention to detail. The poisonous parts of the fish, such as the liver and ovaries, must be carefully removed and discarded, while the remaining flesh is sliced into thin, delicate pieces that are typically served as sashimi. The serving of fugu is often a luxurious and expensive experience and is seen as a badge of honor for those who are brave enough to try it.

Consuming fugu can be risky, as even a small amount of the toxin can be lethal. However, when prepared by a skilled and licensed chef, fugu is considered safe to eat. To ensure safety, the Japanese government strictly regulates the licensing and training of fugu chefs, and restaurants that serve fugu are subject to regular inspections.
Fugu is a delicacy in Japan that is highly prized for its delicate flavor and texture. However, due to its potentially deadly toxicity, it is not something to be taken lightly and should only be consumed at reputable restaurants that employ trained and licensed fugu chefs.

Meaning of rice in Japan
Rice is a staple food in Japan and has been a fundamental part of the country's cuisine and culture for centuries. Here are a few reasons why rice is so popular in Japan:
- Historical and cultural significance: Rice has been a symbol of prosperity, health, and good fortune in Japan for centuries. It has played a central role in Japanese traditions, rituals, and celebrations, and is an integral part of the country's cultural identity.
- Climate and geography: Japan's temperate climate and abundant rainfall make it well-suited for growing rice. Rice paddies are a common sight in rural areas of Japan, and the crop is a key agricultural product for the country.
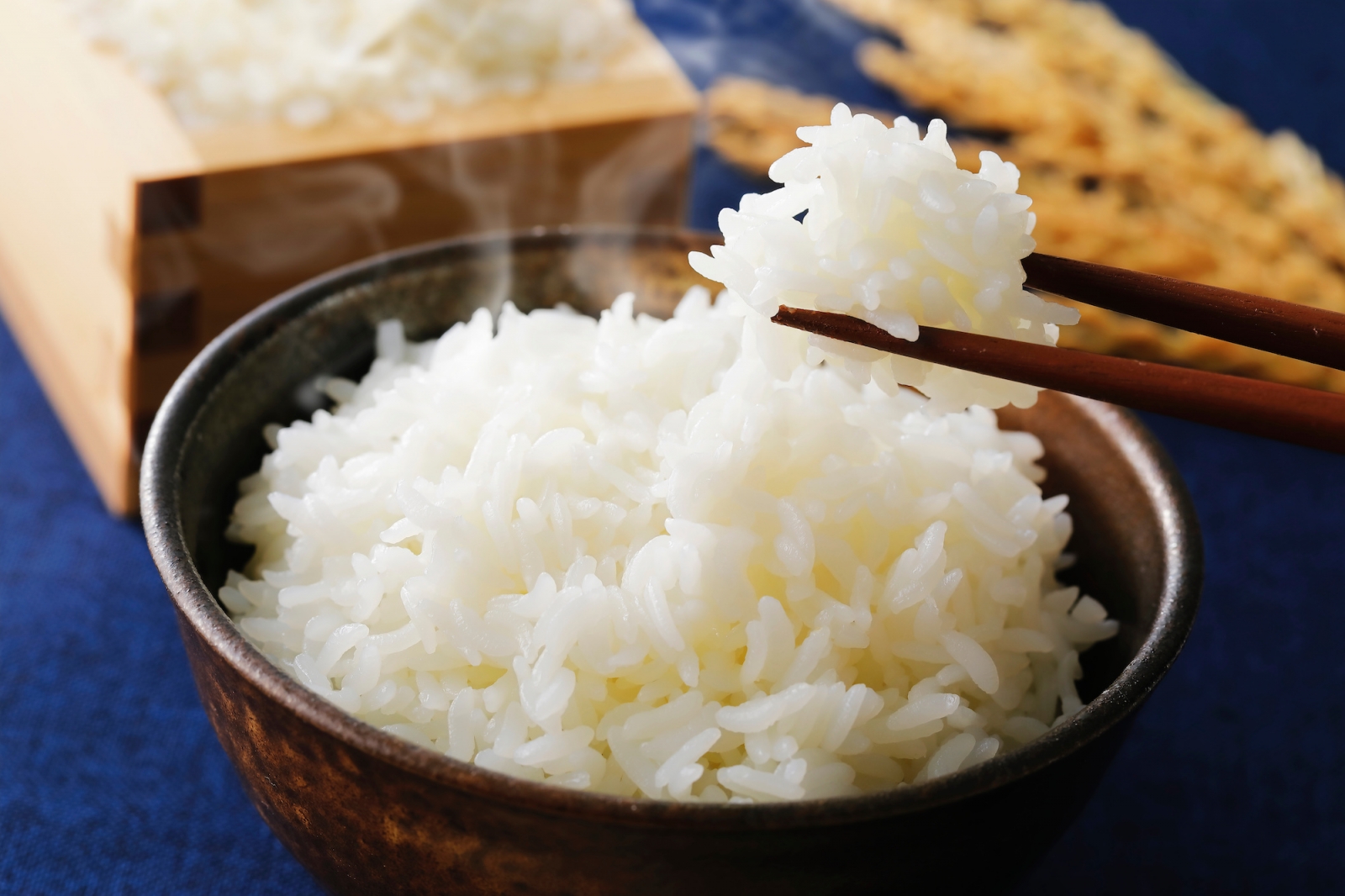

- Nutritional value: Rice is a rich source of carbohydrates, which are essential for providing energy and fueling the body. It is also low in fat and high in fiber, making it a healthy and nutritious food choice.
- Versatility: Rice is a versatile ingredient that can be used in a variety of dishes, from sushi and onigiri to rice bowls and stews. It is also a common accompaniment to many other Japanese dishes, such as tempura and grilled fish.
Rice has played a vital role in Japan's history and culture and continues to be a staple food in the country today. Its popularity can be attributed to a combination of cultural significance, agricultural suitability, nutritional value, and versatility in the kitchen.

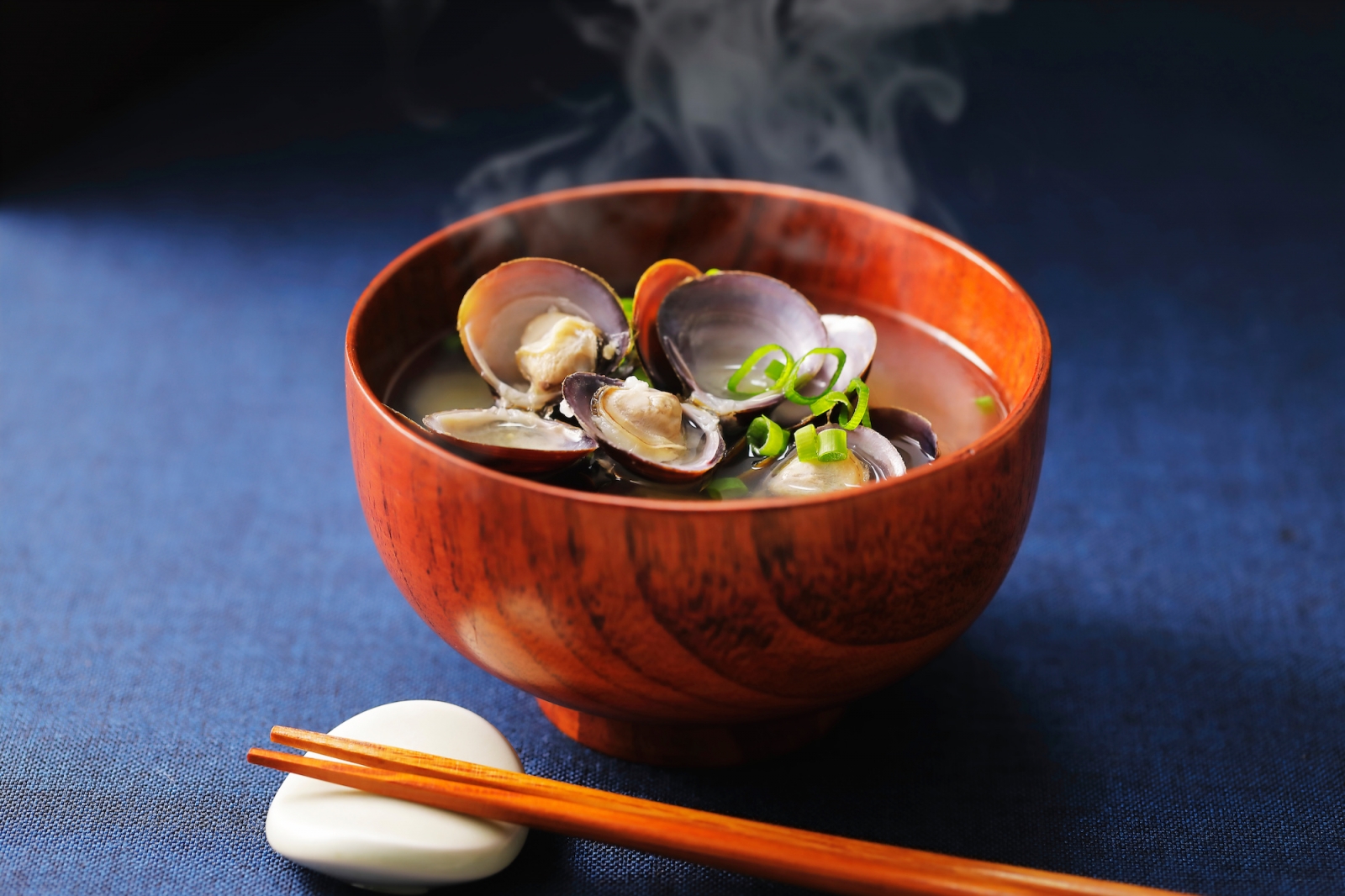
Mollusks forever
There are many different types of mollusks that are eaten in Japan. Some of the most popular edible mollusks include:
- Clams (shijimi): Small, sweet clams that are often used in soups and stews.

- Oysters (kaki): Large, plump oysters that are typically served raw, grilled, or fried.
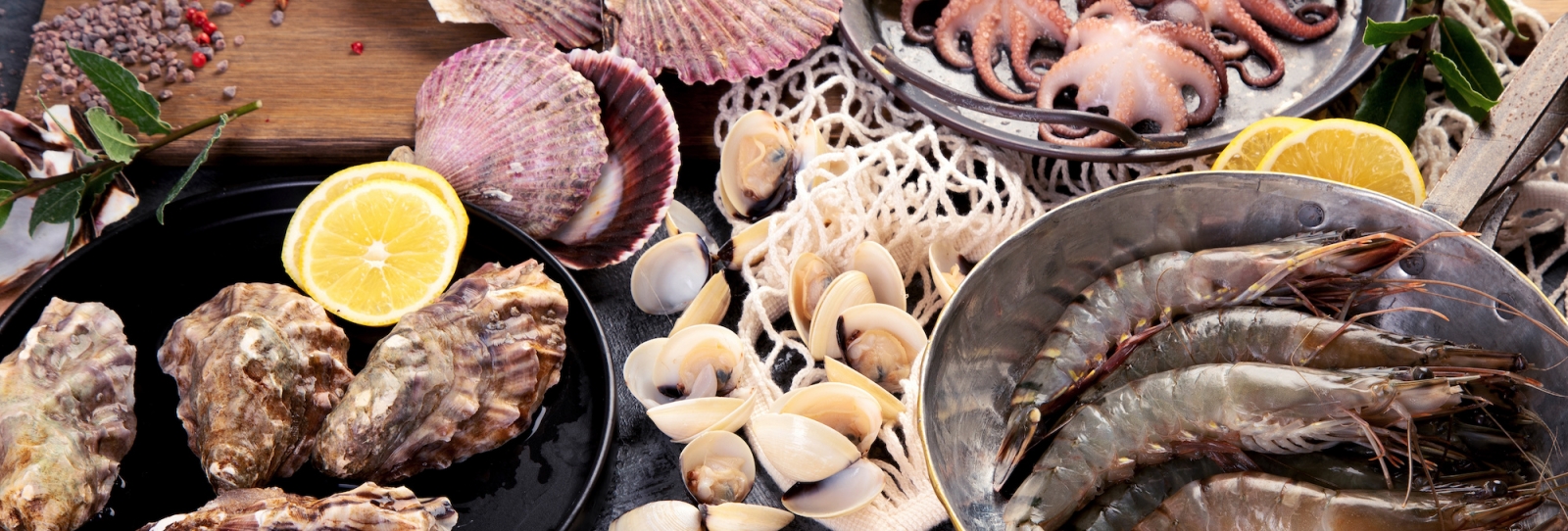

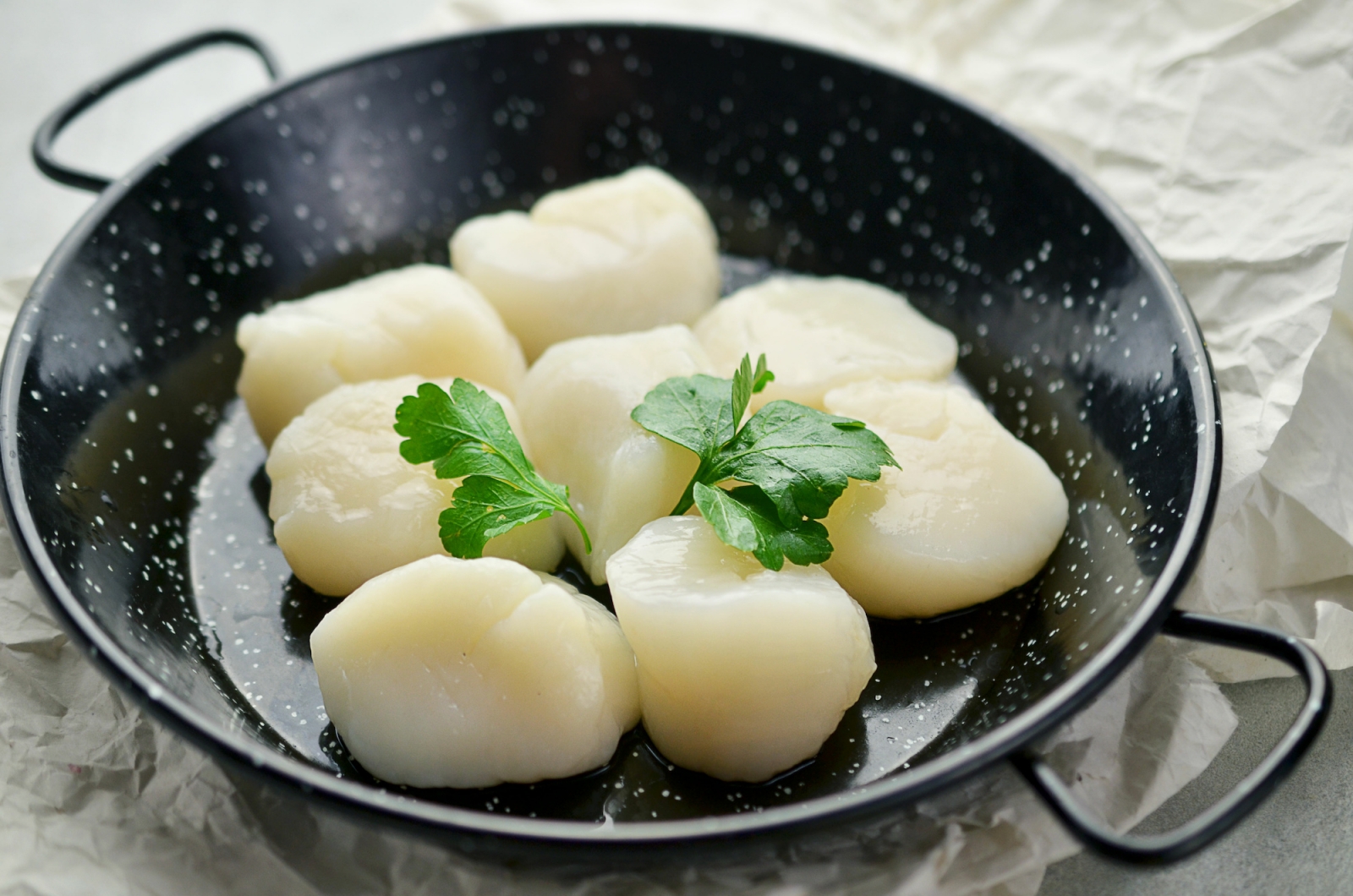
- Scallop (hotate): Large, succulent scallops that are often grilled or served raw as sashimi.

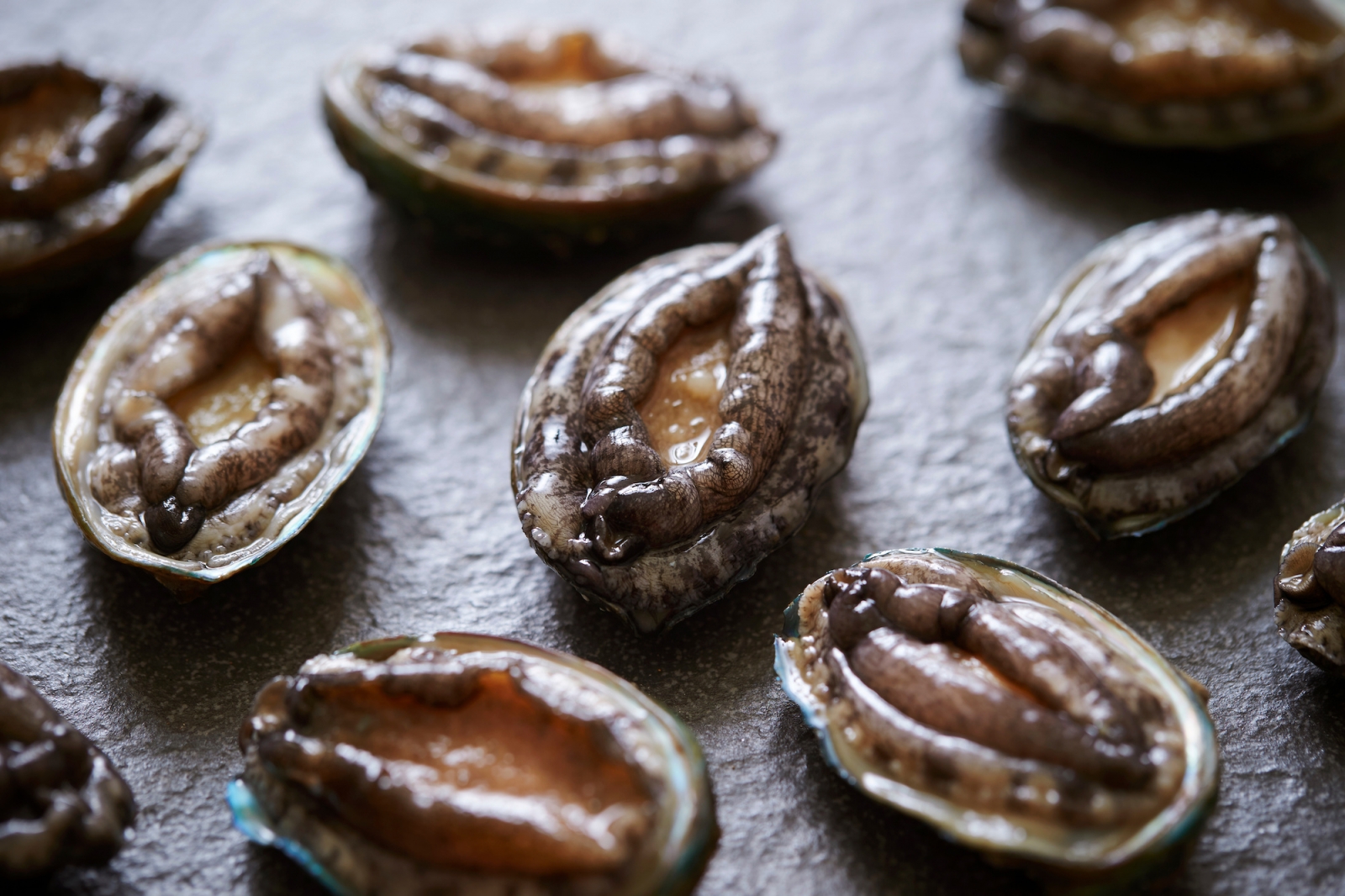
- Abalone (awabi): A large sea snail that is considered a delicacy in Japan. It is typically grilled or steamed and served with a variety of seasonings.

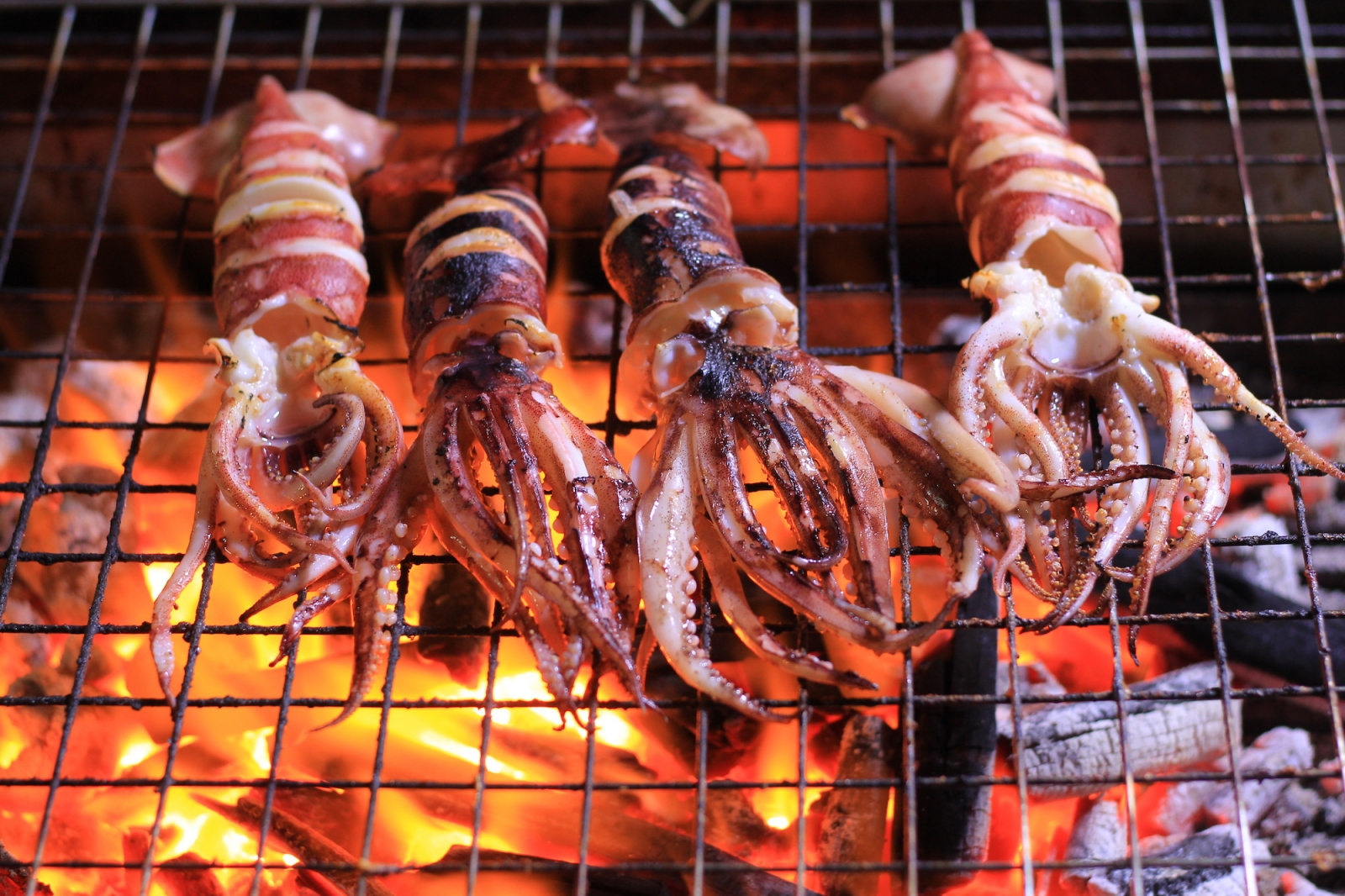
- Squid (ika): A versatile mollusk that is often used in sushi, sashimi, and tempura.

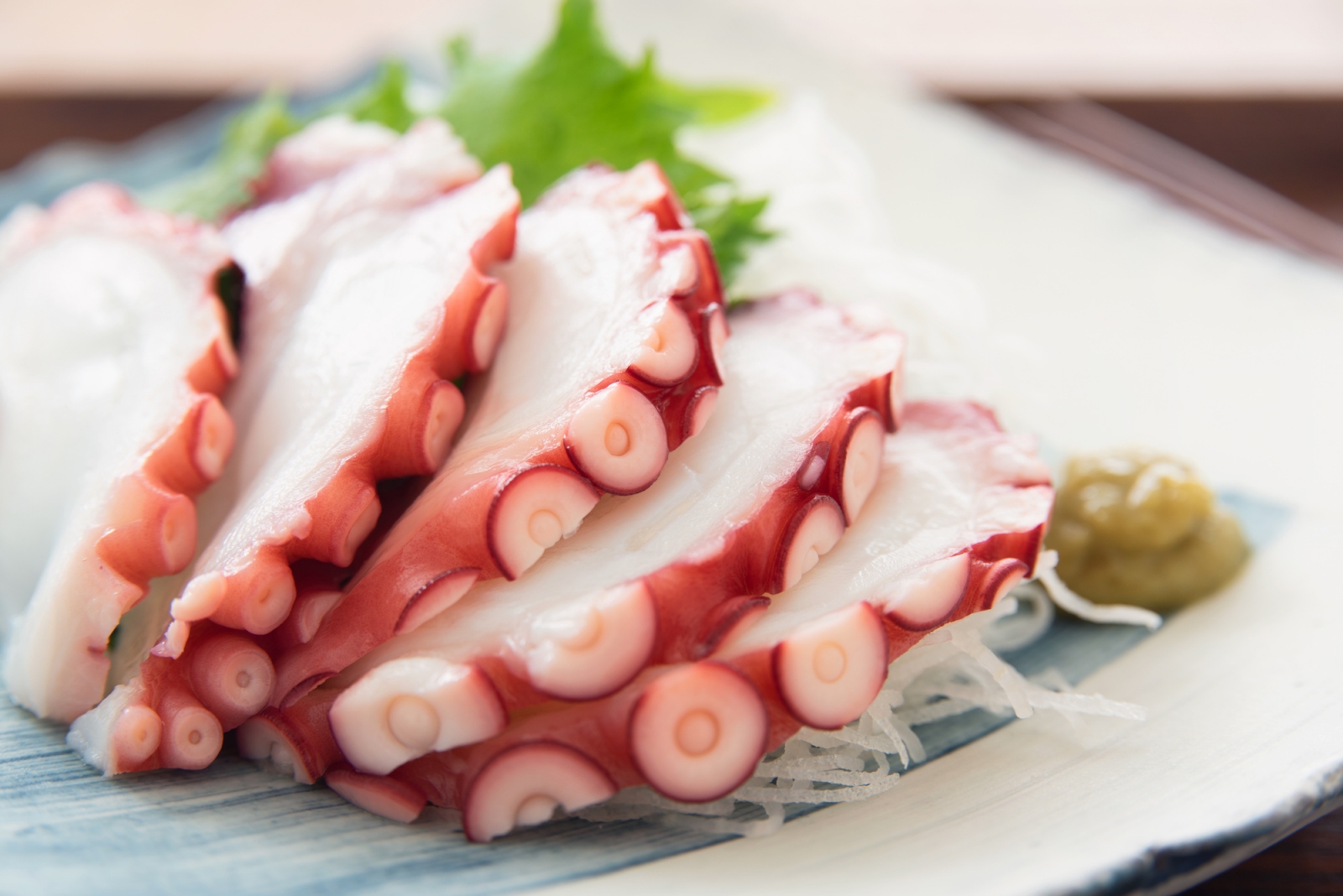
- Octopus (tako): Another popular mollusk that is used in a variety of dishes, including sushi, sashimi, and takoyaki (a popular street food).

- Sea snails (tsubugai): A small, spiral-shaped sea snail that is often used in soups and stews.

These are just a few examples of the many different types of edible mollusks that can be found in Japan. Mollusks are a popular and important part of Japanese cuisine and are enjoyed in a variety of dishes throughout the country.

Why is seafood so healthy?
Seafood is considered to be highly nutritious and beneficial for human health due to a variety of factors. Here are a few reasons why seafood is considered to be good for the human body:
- High in omega-3 fatty acids: Seafood, especially fatty fish such as salmon, tuna, and mackerel, is a rich source of omega-3 fatty acids. These essential fatty acids are important for brain function, heart health, and reducing inflammation in the body.
- Low in saturated fat: Seafood is generally low in saturated fat, which is a type of fat that is linked to an increased risk of heart disease and other health problems.

- Rich in protein: Seafood is a rich source of high-quality protein, which is essential for building and repairing muscle and other tissues in the body.
- Rich in vitamins and minerals: Seafood is a good source of many important vitamins and minerals, including vitamin D, vitamin B12, iron, zinc, and selenium.
- May reduce the risk of certain diseases: Consuming seafood has been linked to a reduced risk of certain diseases, including heart disease, stroke, and dementia.
Seafood is a highly nutritious food that can provide a wide range of health benefits. However, it's important to note that some types of seafood can contain high levels of mercury or other contaminants, so it's important to choose seafood that is low in contaminants and from sustainable sources.

Japanese drinks for Japanese food
When it comes to pairing drinks with Japanese cuisine, there are a few options that are particularly well-suited to complement the flavors and textures of the food. Here are some popular drink pairings for Japanese food:
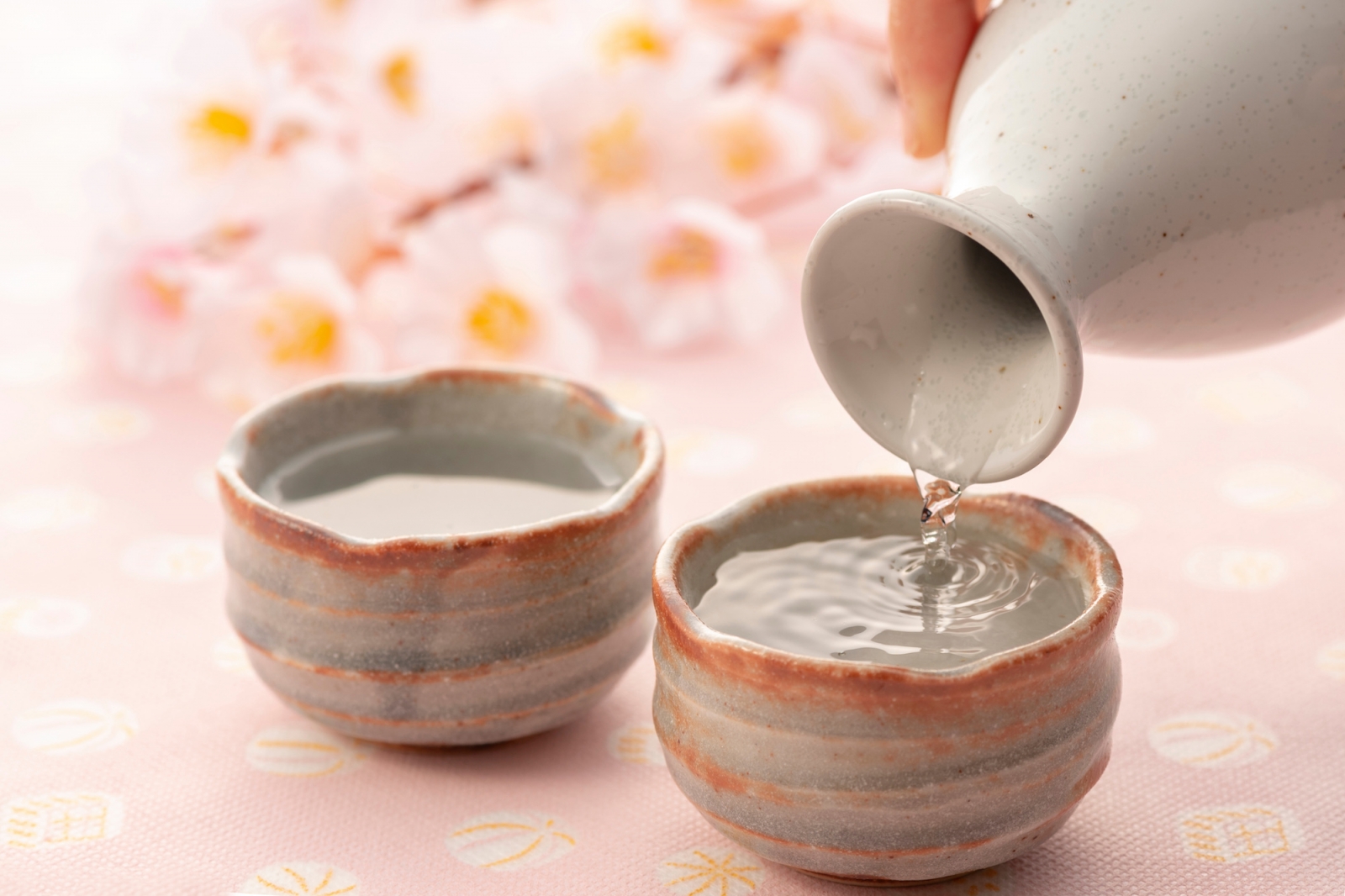
- Sake is a traditional Japanese rice wine that is often served with Japanese cuisine. It is a versatile drink that can be paired with a variety of dishes, from sushi and sashimi to grilled meats and vegetables. Sake is available in a range of styles, from dry to sweet, and can be served warm or cold.

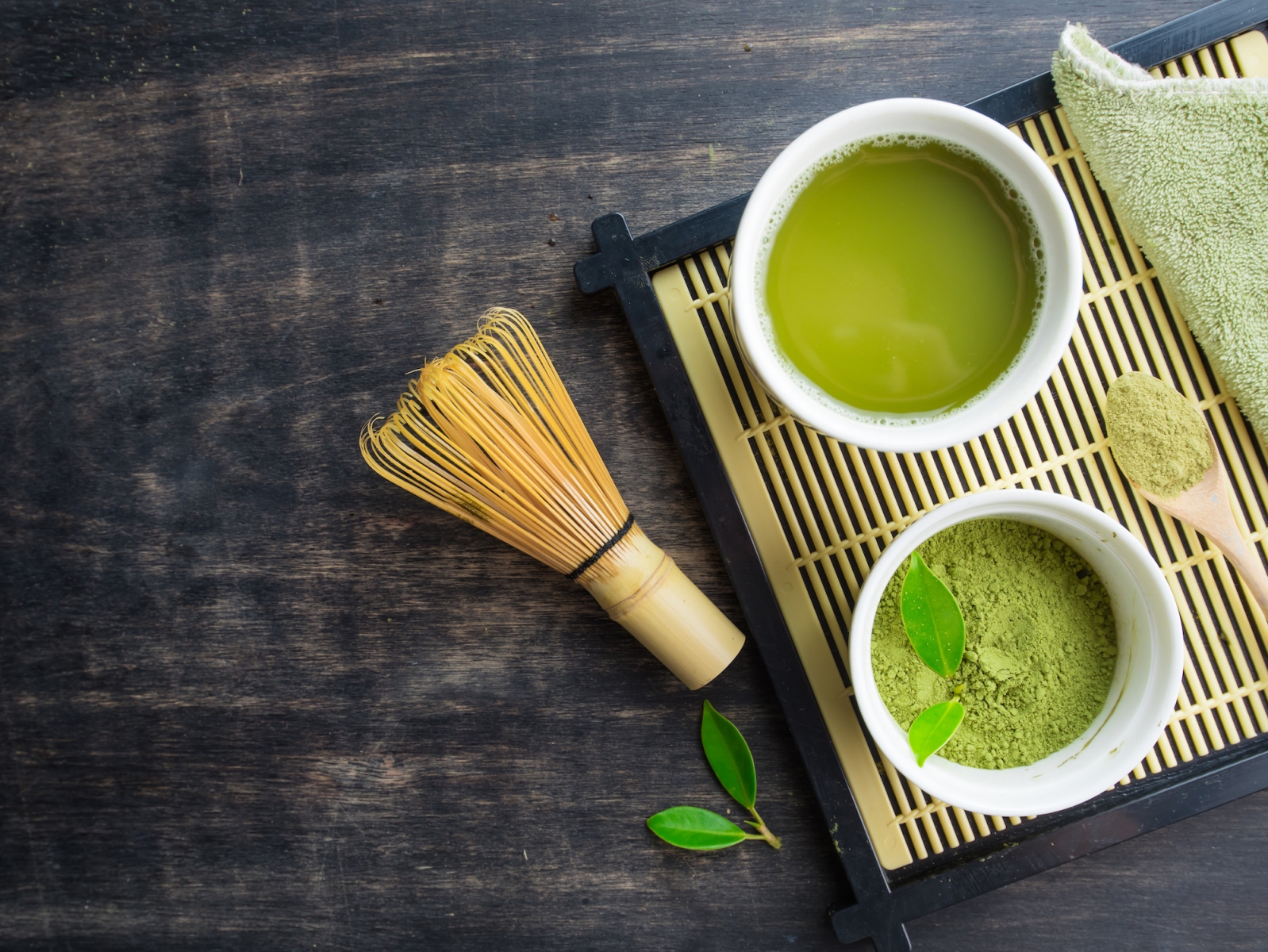
- Green tea is a common beverage in Japan that is often served with meals. Its light, grassy flavor can complement the subtle flavors of Japanese cuisine, and its natural bitterness can help to refresh the palate between bites.

- Japanese beer, such as Sapporo or Asahi, is a popular pairing for many types of Japanese cuisine, including tempura, yakitori, and ramen. The crisp, refreshing flavor of beer can help to cut through the richness of the food.

- Shochu is a Japanese distilled spirit that is often served with Japanese cuisine. It has a lower alcohol content than other spirits, such as sake or whiskey, and is often enjoyed on the rocks or mixed with soda water.

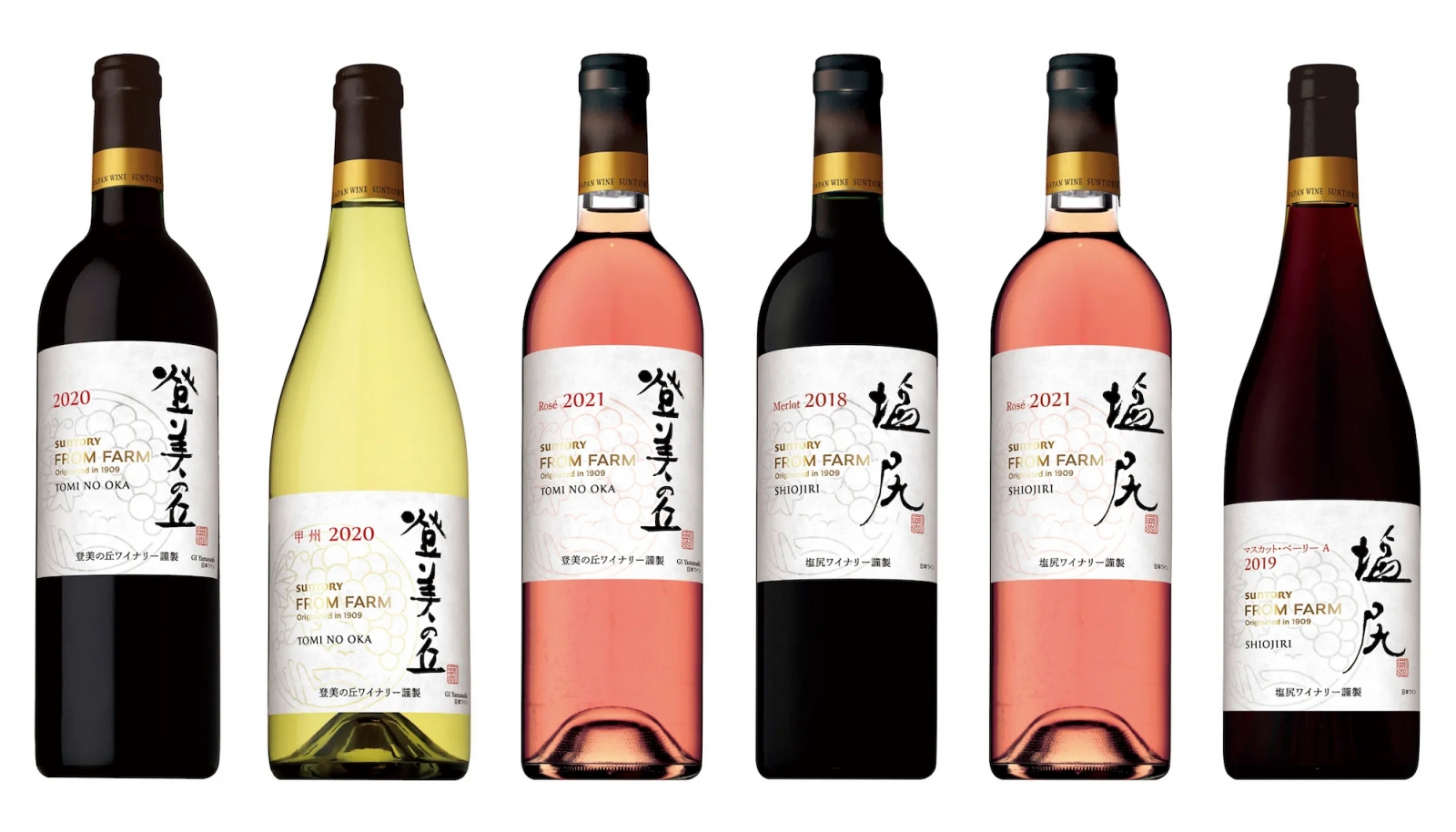
- While not traditional, wine can also be a good pairing with Japanese cuisine. Light, crisp white wines, such as Riesling or Sauvignon Blanc, can complement the delicate flavors of sushi and sashimi, while red wines can pair well with heartier dishes such as yakitori or grilled meats.

The best drink pairing for Japanese cuisine will depend on the specific dish and your personal preferences. Experimenting with different pairings can be a fun and delicious way to explore the world of Japanese cuisine.
Recommendations for non-Japanese tourists who want to try Japanese food for the first time!
If you're a non-Japanese tourist visiting Japan for the first time and want to try Japanese food, here are a few recommendations to help you get started:
- Start with sushi: Sushi is one of the most famous and popular Japanese dishes, and it's a great way to sample a variety of flavors and textures. If you're new to sushi, start with some of the more familiar varieties, such as salmon or tuna, and work your way up to more adventurous options.
- Try ramen: Ramen is a hearty and comforting noodle soup that is beloved in Japan. It's a great option if you're looking for a filling meal that won't break the bank. Look for a popular local ramen shop, and be prepared to wait in line, as many of the best places have long queues.
- Don't be afraid to try street food: Japanese street food is delicious and affordable, and it's a great way to sample a variety of different dishes. Look for food stalls or markets that offer a range of options, such as takoyaki (octopus balls), yakitori (grilled skewers), and okonomiyaki (savory pancakes).
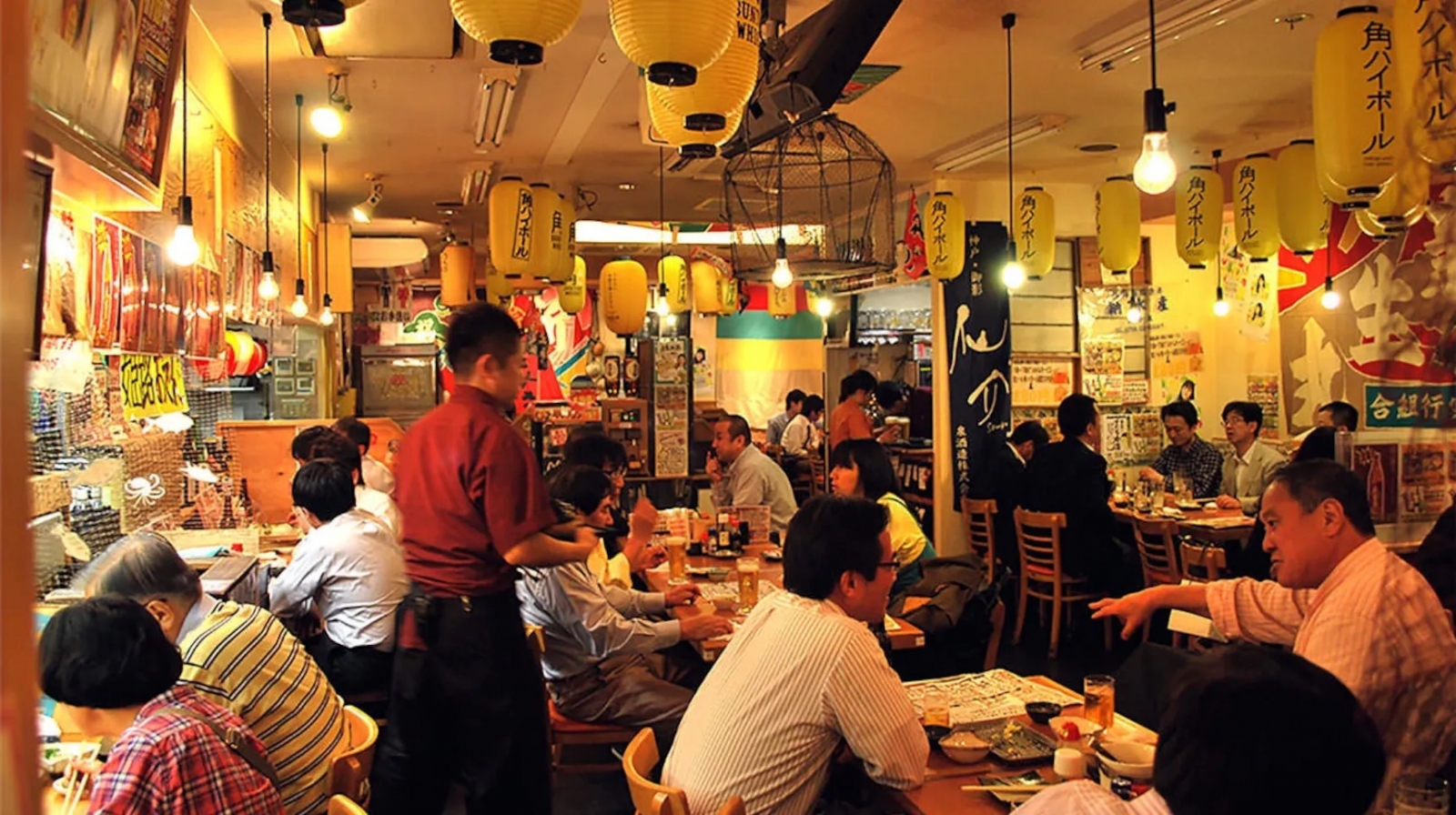

- Visit a traditional izakaya: An izakaya is a type of Japanese pub that serves a range of small plates and drinks. It's a great place to sample a variety of dishes and get a feel for the local culture. Look for an izakaya that is popular with locals, and be prepared to try some new and unusual dishes.
- Ask for recommendations from your local English-speaking tour guide in Tokyo or other Japanese cities: Japanese cuisine is incredibly diverse, and there are many regional specialties and unique dishes to try. Don't be afraid to ask locals for recommendations or to try something that you've never heard of before.
Japanese cuisine is incredibly varied and delicious, and there is something for everyone to enjoy. Whether you're a seasoned foodie or a first-time visitor, be sure to try as many different dishes as possible and explore the amazing flavors and textures of Japanese food.

In search of UMAMI
Umami is one of the five basic tastes, alongside sweet, sour, salty, and bitter. It is a savory or meaty taste that is often described as "deliciousness" or "yummy" in English. Umami is a Japanese word that means "pleasant savory taste," and it was first identified as a distinct taste by Japanese chemist Kikunae Ikeda in 1908.
The umami taste is created by the presence of glutamic acid, an amino acid that is naturally found in many foods, particularly in protein-rich foods such as meat, fish, and dairy products. In addition to glutamic acid, other compounds such as inosinate and guanylate can also contribute to the umami taste.
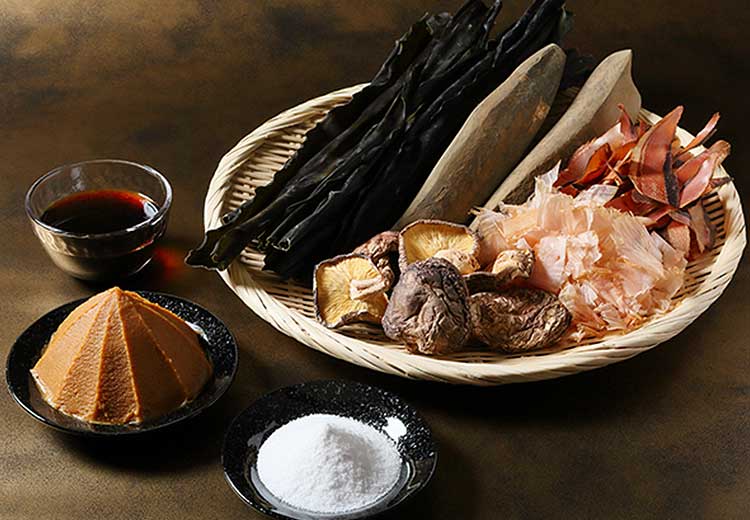

Umami is a complex taste that can enhance the flavors of other ingredients and make food taste more delicious. It is often used in cooking to add depth and richness to dishes, and it is a key component of many traditional Japanese foods, such as miso soup, soy sauce, and dashi broth. Umami is also found in many non-Japanese foods, such as parmesan cheese, tomatoes, and mushrooms.
In recent years, umami has gained increasing attention in the culinary world, with many chefs and food scientists exploring its potential as a flavor enhancer and a way to create more delicious and satisfying foods. Try as many Japanese various dishes as you can and be sure, finally - you will find your own UMAMI!

Read our previous article Argentinian Winery Tours: A Wine Trip
Read our next article Hot safari destinations in Africa